Box Hill South
The Built Environment - Box Hill
We grew up in Box Hill South in close proximity to Surrey Hills where our family has had an association for five generations. 28 Moore Street was our family home. We all spent our childhood and early adult years there, before moving out on our own. The family ventured out into Box Hill in 1946 when our parents bought a block of land in a new subdivision. They paid one hundred pounds plus ten pounds in taxes. Jim and Alice also looked further out in Donvale, where, for a fraction of the cost, they could have purchased two acres of bush. Unfortunately this was not an option as there was no public transport and we did not own a car.
After the war, Box Hill South was opened up for new housing. The City of Box Hill revised its land valuation system and residential subdivision started to boom across the municipality. The small holdings of mixed farming and orchards, were quickly replaced by the unmade road network of the subdivisions. Electricity and gas were provided, but no sewerage until the 1950’s, so it was outside toilets for all.
Our parents could not afford to have the house built, so Jim decided to build it himself. He bought a book on basic carpentry and the tools, all hand tools of course, and proceeded to build. The house is still there today, straight as a die.
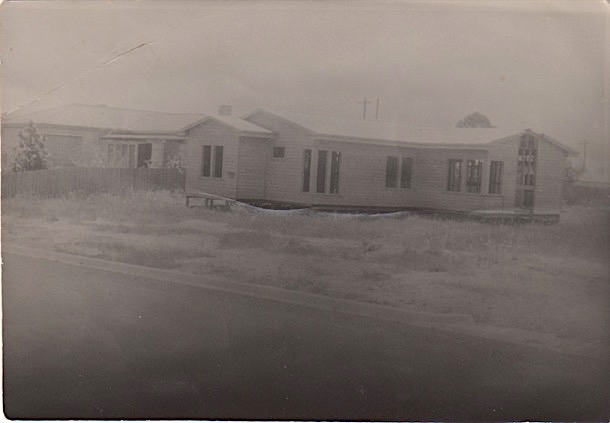

It was a very liveable and rather nice design, set on stumps, weatherboard cladding and with a low slung, pitched roof. It had the standard three bedrooms, one bathroom, kitchen, dining room, lounge room and laundry. When first built there was an outside toilet attached to the single garage that also had a chook pen attached to it.
Over time, the surrounding paddocks filled with houses and our house changed a little too. The view of the Dandenongs from the french doors in the lounge room disappeared, the toilet moved inside and our grandparents built a flat on the back. The addition of the rumpus room and flat spoilt the spaciousness of the living rooms and the back garden. The old weatherboard garage, toilet and chook pen were removed and a new double garage and new chook pen took the new additions to the back fence.
Little appears to have changed externally to the house since Mum sold it about 1981.

When we were children, Wattle Park itself consisted of large trees with mown grass underneath, like a traditional park, but with native trees and grasses. It was owned and maintained by the Tramways Board, responsible for the tram system in Melbourne. The Tramways brass band played in a rotunda every Sunday in the park. Nowadays those grasses are no longer mown. It looks much more like remnant bushland.
The 137 acres opened as a public park in 1917.

The chalet, designed and built by a Tramways architect, opened in 1928. it was promoted as a dance hall and wedding reception venue and, amazingly, it still is. It is listed on both the Heritage Victoria and National Trust Registers.
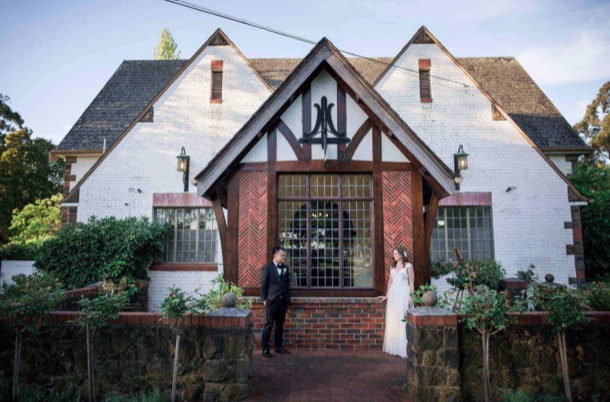
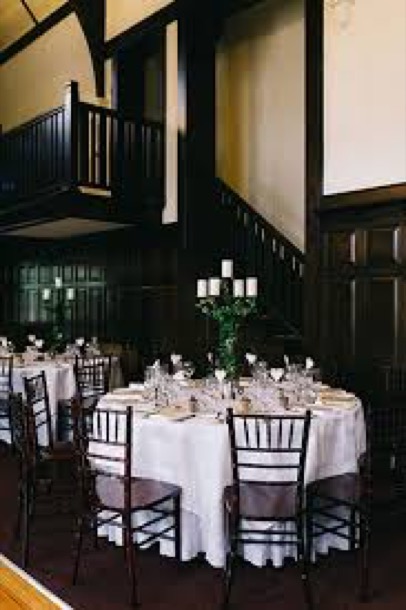


Our own parents’ wedding reception was held there in 1945, after they had been married at the Wyclif Surrey Hills Congregationalist Church in Surrey Hills.

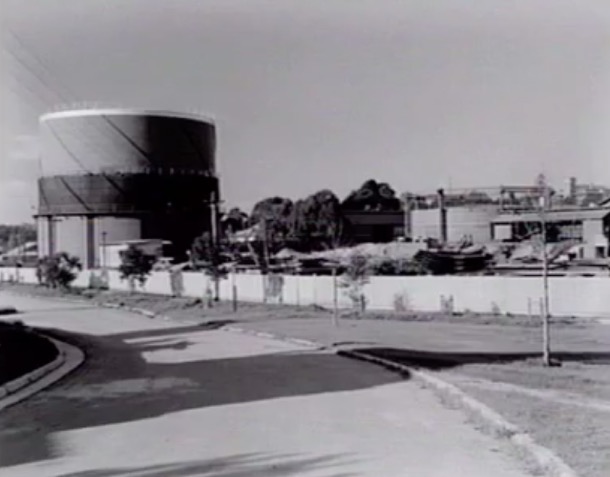
Box Hill Gasworks is now gone, but it was an important part of our parents' history. It was built early in the history of Box Hill:
7/1/1890 The Argus
Some twelve months ago the Nunawading and Boroondara councils granted permission to Mr. Thomas Coates, hydraulic engineer, to lay down gas mains in the streets of the two shires. Mr. Coates purchased an eligible site near Elgar road, Box Hill, upon which to erect the gasometer and the other necessary buildings. At the present time all the mains have been laid down in the shires named, and Mr. Coates is now in a position to light up Surrey Hills and Box Hill with gas. The local works are of such a nature that Mr. Coates contemplates being able to supply the wants of the district for many years to come without enlarging the gasworks. Last night a trial was made in Box Hill and Surrey Hills, when the corporation lamps were lit with gas for the first time. Illumination works were erected at the intersection of the leading streets. The trial was considered a very favourable one, the gas burning bright and clear. In connection with the lighting of these shires with gas a public banquet will be held in Surrey Hills next Monday night.
Over time three gasometers were built.

We don't know exactly when Jim started work at the Box Hill Gasworks, but in 1945 he left the Maribinong Munitions factory, where he had spent the war years. It was that year when our parents married and Jim moved into his in-laws’ Surrey Hills house. Soon after, he started work at the gas works as an analytical chemist. He worked there until began teaching in 1954.
Sue remembers him riding his bicycle to work, and later, a motorbike.
He worked in the laboratory, doing things like checking the calorific value of the gas.
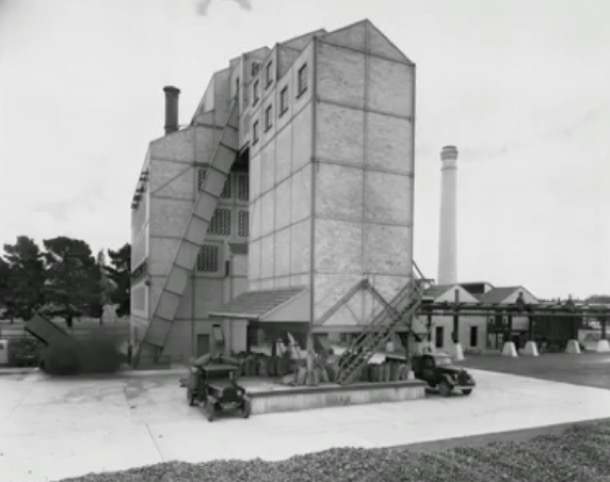
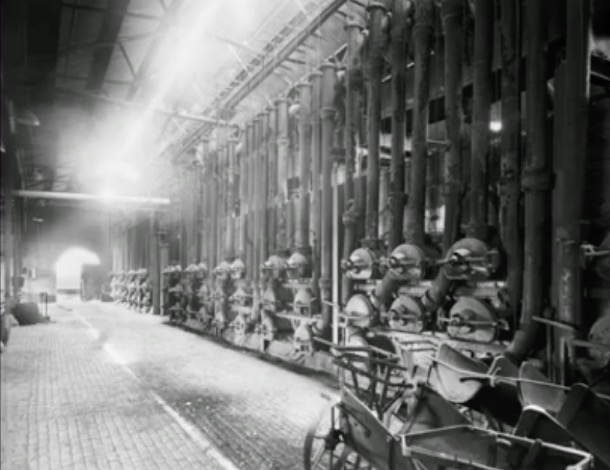


Melbourne’s gas supply was made from Latrobe Valley brown coal, sent by rail to the various gasworks, owned by Colonial Gas Company. Box Hill was one of the biggest. As Melbourne expanded after the war, the demand for gas meant that the various gas works were very busy.
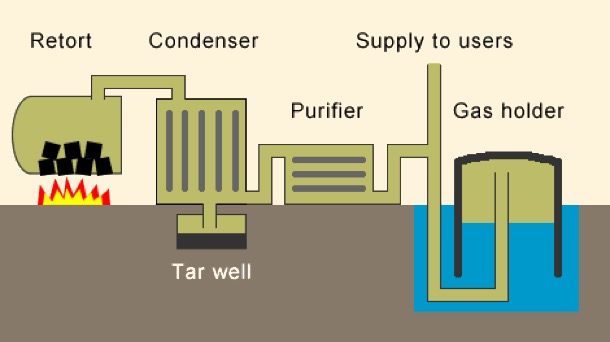
But, by 1960, substantial natural gas reserves had been discovered around Australia. Over the next five years all the Gas plants in Melbourne had closed down, and over 1000 workers were made redundant, by the discovery of natural gas deposit in Bass Strait. Over one million gas appliances in Melbourne were converted to natural gas in 1968. We remember the conversion time. There must have been plenty of publicity. Natural gas has no smell, and, for safety, they put in an additive to make it smell quite strongly. The flame was slightly different, but all the existing burners still worked.
The Gas Works are long gone. Box Hill Institute now occupies the site.

One of the fortnightly highlights in our simple lives was a trip to Box Hill Library. We loved this excursion, as we spent many hours reading on our beds. Books were expensive and we only owned a few. We had to rely on the Library so that we could finish our favourite series like Famous Five and the Billabong Books. It was very exciting if the next book in the series was on the shelf.

This small brick building was opposite the Town Hall at the end of the shopping centre. Whitehorse Road always had a wide, tree lined median strip, as it does today, and the library was right in the middle. It was later replaced by a grand modern library, but the small brick building is still there.
In our childhood, a trip to Box Hill shopping centre was quite an excursion, involving a four mile walk. In 2019 Google Maps says it takes thirty two minutes, but with small legs and a pusher as well, maybe it took a little longer. I remember it was fun and not arduous at all. The route went through suburban streets until Canterbury Road and from there it was ovals and open ground.
Box Hill Brickworks was one of the best sights on the walk to Box Hill, as the brickworks were still in full production. We marvelled at how small the men and carts were at the bottom of the quarry, and watched the procession of carts pass up and down the steep rail track to the actual brick works.
Box Hill Brickworks was founded in 1884 and was one of fifty or so brickworks throughout Melbourne, producing bricks, tiles and pipes for the building boom and ever expanding city. During the working life of the brickworks the clay was extracted from two clay holes or quarries. The first became Surrey Dive which became a popular swimming venue, but off limits to us. Sometimes however, we also gave ourselves the horrors, looking at green, mysterious waters. There were rumours of 'the dive' being bottomless and of swimmers disappearing in its murky depths. One story was of a man who took a very deep dive off the cliff side and simply disappeared. Some time later his body surfaced in Blackburn Lake, five kilometres away. No wonder we looked in awe and horror through the fence.
Today Surrey Dive is an attractive small urban lake used for swimming and remote controlled boat races.. A walking track around the ‘old dive’ and the brick works is planted with indigenous vegetation and a relaxing and attractive area.

The other clay hole was the quarry that was in operation doing our childhood. It was adjacent to the brickworks and kiln, now derelict but still heritage listed. Unfortunately no restoration work has been carried out. The kiln itself was a massive, red brick building constructed on two levels and, of course, with a huge brick chimney.
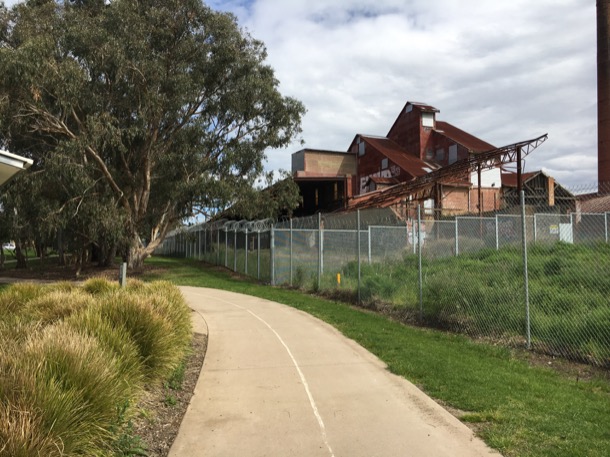

The quarry that was still in full production in our childhood, is now completely filled in. That cavernous hole in the ground is now a large mound covered in every weed known to man. On the horizon above the weeds, are the sky scrapers of twenty-first century Box Hill.

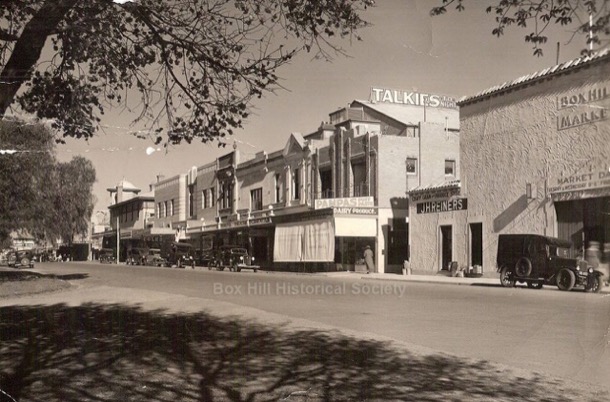
Box Hill shopping centre developed as a commercial centre, as soon as the railway line between Hawthorn and Lilydale was finished in 1862. It became an important transport hub for the eastern suburbs and beyond. During our childhood, Box Hill was the shopping destination for a big purchases. For instance, I can remember choosing a ‘walking’ doll with opening and closing eyes for a birthday present and the excitement of choosing a winter coat with a brown velvet collar. Another favourite shop was the delicatessen where such delicacies as rollmops, sauerkraut and frankfurters could be bought. Amongst the many single fronted small businesses were several large shops such as Taits haberdashery on the corner of Whitehorse Road and Station Street and Maples furniture shop. We also had a Coles variety store that sold anything from socks and singles to cosmetics, and MacEwans Hardware whose slogan was, “You can do it with McEwans because we’ve got a million things.”


This is a photograph of Box Hill Station and the surrounding shopping precinct in the 1960s. In the centre of the photograph is the old station, that is now underground. Today, above ground, occupying the whole block surrounding the old station, is Box Hill Central and surrounding shopping malls. The signal box, the tall structure on the left of the railway gates is now occupied by the thirty-six storey golden residential tower, called Sky-One.

In the twenty-first century, Box Hill, as a commercial centre and transport hub, continues to influence the built environment around it, as you have no doubt witnessed. Officially designated as a development hub, Box Hill now sports high rise office and apartment towers. The streets we once drove down are now shopping malls, the station is underground, the railway gates are long gone and the strip shops have been replaced by a multi storey modern shopping centre. When we were children the shopping crowds were white and Anglo-Saxon. Today they are predominately Asian and the shops and restaurants reflect the change in population.

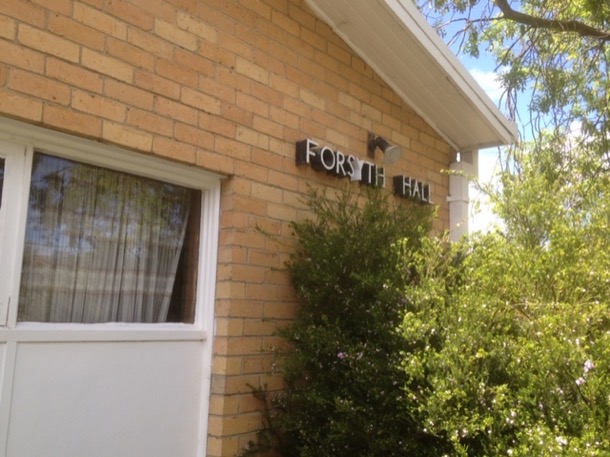
When we, as a family, first started going to the local Presbyterian church, it was called Presbyterian, Wattle Park. We had PWP embroidered on the front of our blue gym uniforms. This was before the advent of the Uniting Church. Church services were held in a cream brick building, called Forsythe Hall.

Attached, behind it, was an older little wooden building. During our childhood, this wooden building, Staley Hall, was used for a kindergarten during weekdays. In the evenings, various groups used it, including church boys’ and girls’ clubs (PBA and PGA) and the mixed club (PFA- Presbyterian Fellowship Association), we went to as teenagers. Sue and I both learnt to dance there, and I broke my front teeth on the heater in that room.
We have many memories of Forsyth Hall… dances, performances, Saturday afternoon movies, gym classes and, of course church services.

Both our parents were Elders of the church. Our mother taught Sunday School, our father ran the PFA for a while, and was on the board of management. The church was their only real friendship group, and was the only social life we had, as a family.
In the early 1960s the church community began the project of building a new church on the site. The size and scale of the project was a source of much disagreement between our father and others on the management committee.
In the end, a very grand architect designed building was commissioned. The new building was designed by well known architects Chandler & Patrick. An 1887 pipe organ was relocated from a church in Melbourne and extensively rebuilt. The new church, renamed St James, opened in 1965.

I loved it, because I sang in the church choir, and it had a choir loft at the back and great acoustics.
The buildings are still there. Sue and I visited as a detour on our “back to school” walk in 2016.

Comments
Decade by Decade
Five hours of Alice and Marge’s family stories finishes with an overview. Strikingly, Alice did most of this by herself, without notes. She was of course, blind by this stage of her life. She had a remarkable ability to condense Australian history neatly into decades, and find the parallels in the family history.
Here is the audio of this from the recordings:
With our more modern education, we have less of a firm grasp of History, and we know that our children, and their children have, and will have, an even sparser knowledge. So we have taken the overview concept, explained a little more fully, and added in our father’s family history and other aspects we have recently discovered.
Alice and Marge finished recounting their family stories at 1950. One of our tasks in this project has been to continue on from then, and so we have done just that. We explore the nineteen fifties, sixties and seventies, linking what was happening in the wider world into our own lives.
1850-1950
Between 1839 and 1872 our ancestors arrived in Australia.They came from both Northern and Southern Ireland, England, Germany and Denmark. All were from humble origins, having worked as agricultural labourers, domestic servants, a baker and an engineer. Some were already married and others met here.
As our ancestors built their new lives in Victoria, the First Australians had already felt the disastrous impact of European contact. There had been violent conflict, the Wurundjeri population had been decimated and the survivors relocated to reserves or camps a ‘suitable' distance away from the growing population of Melbourne and outlying settlements. In 1844, when the Bourkes took up their selection at Pakenham, they were the first white settlers in the area and the “blacks camp” by the river was noted in Catherine’s memoir. Several years later, Adam Rye, from the other side of the family, was robbed by a party of ’50 blacks’. The newspaper report notes that ‘the blacks at this time were very treacherous’.
With the discovery of gold, in New South Wales and Victoria, there was a huge increase in population and in wealth.
Victoria benefitted the most. Melbourne became Australia’s largest city, with a huge land boom. Grand old buildings like the Melbourne town hall and exhibition buildings are reminders of those glory days.

The increase in population, rapid development and the attraction of the goldfields led to a shortage of workers. This meant great job opportunities at every level. It also put workers in a good bargaining position.Trade Unions developed and working conditions were the best in the world. Australia was an egalitarian workers’ paradise.
Small businessmen, like publicans, bakers and lawyers, prospered with the growth in Melbourne. For farmers, it meant bigger markets, more mouths to feed. The growth in country towns, better roads and railway development made life in the country less difficult.
Engineers had a lot of work, with the sudden development of infrastructure, and property developers were run off their feet. Our great, great grandfather, a young engineer from England, was building bridges in the expanding colony. While building the bridge across the Barwon River, his son was born, his birth unregistered.
Back in ‘Marvellous Melbourne’ our grandmother’s grandparents who had arrived from Belfast, were developing St Kilda: building large houses and public buildings for those who were prospering in the boom town.
On the land, our maternal ancestor Adam Rye, who had survived the attack by ’50 blacks’, settled in Geelong and worked as a farm labourer. He was later gripped by gold fever and went north to seek his fortune, only to be held up by bushrangers and lose his meagre pickings. His daughter married a German immigrant, Dau, and they settled on a mixed farm at Wandong. Here they raised seventeen children and supplied food to the growing population.

Meanwhile our paternal forbears, also on the land, were making their mark in Gippsland and North Central Victoria. In Pakenham the Irish Bourkes were building their family of thirteen children, and now owned Bourke’s Hotel. They were becoming significant landowners and community members, as they set about acquiring land, marrying their daughters well and establishing their sons on large and prosperous properties. They also served their community in local Government and built the horse racing industry in Pakenham.
1858 Land Sales, Michael Bourke's purchases:

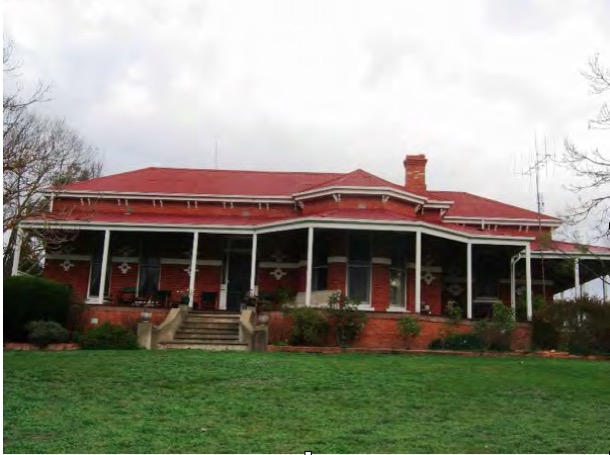
The McCormacks and Hamiltons, in North Central Victoria were also acquiring and working large grazing properties, in the Goulburn Valley. They too were pillars of the local Catholic Church and community. Our grandmother was born at Balham Hill, at Molesworth, pictured below.

Melbourne became the financial centre of Australia and New Zealand. The Pakenham Bourkes’ fourth son, our great grandfather, was part of this world. He had moved to Parkville and built his law career in this thriving city. Australians were growing in confidence and the young nation was showing signs of an interest in its own identity. This was the era of Henry Lawson and Banjo Patterson, who wrote about the characters of ‘the bush’. At the same time, Tom Roberts and his paintings glorified the unique Australian landscape and the men and women who toiled there. This growing sense of identity and of nationhood is reflected in the moves for independence from Great Britain. During this era of optimism and hope our grandparents were small children, and their families were well established in both country Victoria and Melbourne.
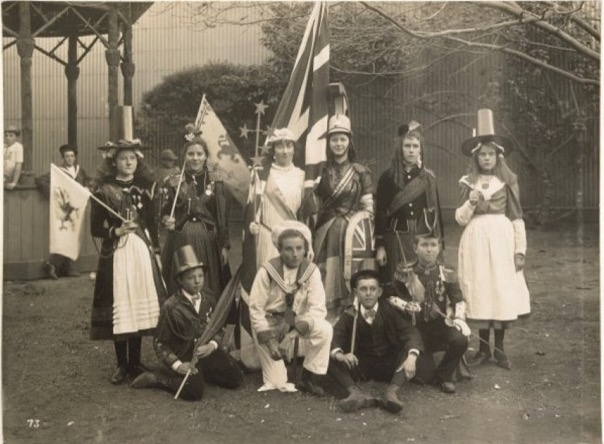
Federation was achieved in 1901, and the country celebrated:

Australia was longer a colony but an independent nation. Melbourne was the largest city in Australia at the time and the second largest city in the Empire (after London). It was fitting that the new Parliament should sit in Melbourne while Canberra was being constructed.
The decade after Federation saw Australian women join the battle for women’s suffrage. White men over 18 in Victoria had had the right to vote since 1858, but women were not granted this right until 1908. Our maternal grandmother, Alfreda, was sixteen when women were granted the right to vote. We imagine she would have approved. She had been engaged in her own battle to pursue her dream of further education; and during this decade she finished her secondary education at Melbourne’s Continuation School, the opening of which marked the beginning of state secondary education in Victoria.
This period of prosperity, optimism, and political and social change ended in the devastation of the Word War 1. We know little of the family’s war service, but three of our maternal grandfather’s uncles served in France, and one lost his life. In the highly charged patriotic atmosphere of the time, and with mounting casualty lists, the war years must have been a difficult time, especially for our grandfather who was considered unfit for service due to ill health. He was deeply upset when given a white feather. Presumably our paternal grandfather being a country doctor, was in a protected occupation.
Our grandparents were all married at the end of this war. Our father’s parents were married in St Patricks Cathedral in a grand affair. Grace and Hugh then settled in Koroit in the Western District, where Hugh was the local doctor.

In contrast our mother’s parents were married in the Methodist Church in Surrey Hills in a small and simple ceremony where the bride did not even wear a wedding dress. At that time Alfreda was working as a teacher and Alf was working in a hardware shop in the city. They also moved to the country, soon after: to Eildon, where hardware supplies were needed for the construction of Eildon Weir.
Our family then lived through the Great Depression of the thirties, formative years for our parents who were by then at school. Our father was boarding at Xavier College and our mother was at Croydon Primary School. By the end of the decade the world was at war again.
During the war in a munitions factory, in Maribyrnong, two very different family histories were to merge into one. One was Irish Catholic, successful and quite wealthy, and the other was staunchly Protestant and relatively poor. One was involved in the Melbourne horse racing scene and the other was teetotal and interested in ideas and the new ‘isms’ that were emerging on the other side of the world. Our parents were married at the end of World War 2.
1950s
Our mother’s view of the 1950s, in her recording, is of a time of burgeoning economic growth and development. To us, it is the decade we first became aware of the world.
Our world was redolent with Australiana, but we were intensely aware of our British heritage, and it dominated our reading, our schooling, our whole culture. A portrait of The Queen hung in our school. Sue remembers keeping a scrap book at home of magazine articles about the Royal Family. She was particularly interested in the corgis. Apparently I had one too, and it contained very many pieces about Princess Margaret.
Enid Blyton Books:

Globally, it was a dangerous world, with the cold war in full swing, and a very real threat of nuclear war. Our parents had quite well developed political opinions, particularly our mother, so we were exposed to adult conversations about the issues of the day. Family friends and neighbours, the Lees, were active in the union movement. They encouraged our parents’ involvement in the movement for “unilateral disarmament” and other left wing activities. I remember our mother’s admiration for an older couple who took a small boat out into the Pacific Ocean to protest the nuclear testing. Bikini Atoll in the Pacific, sixty years on, is still a no go zone from the USA nuclear tests carried out there up until 1958.

This was the time of McCarthyism in America, and Australian political attempts to ban the Australian Communist Party: a divisive time, where everyday people had strong opinions one way or the other. Sue remembers Prime Minister Menzies as “the devil incarnate”.
The Campaign for Nuclear Disarmament became overwhelmed in the 1960s by anti Vietnam War action, but it was an important political movement of the 1950s. The familiar “Ban the Bomb”, or “Peace” symbol was invented in 1958, as a symbolic representation of ND (Nuclear Disarmament)

Our family was, by today’s standards, quite poor, but this did not impinge on our life, at this time. We were well fed, we had a stay at home mother who looked after us and the struggle to pay bills was not part of our conscious experience. As far as we children knew, we were neither poorer nor better off than our neighbours, with the exception of the family in the housing commission house nearby, whose son had polio and who didn’t always have enough to eat. The world, as we observed it in our daily life, was largely classless. Perhaps Australia at this time really was the egalitarian workers’ paradise it purported to be, to prospective migrants in Britain. (only whites of course)
Nevertheless, we knew about the religious and economic differences within our family: that our father’s relatives were wealthy and that we were not, because our parents’ union was a “mixed marriage” and very disapproved of. We were very aware of their Catholicism and our Protestantism, and that we were not as close to our grandmother as our cousins were.
Our father during the 1950s, went from working as an industrial chemist by day, and studying by night, to full time teaching. We got our first car, a television and a refrigerator. By the end of the decade there had been four children born. It was busy, but simple life, encumbered by very little “stuff”.
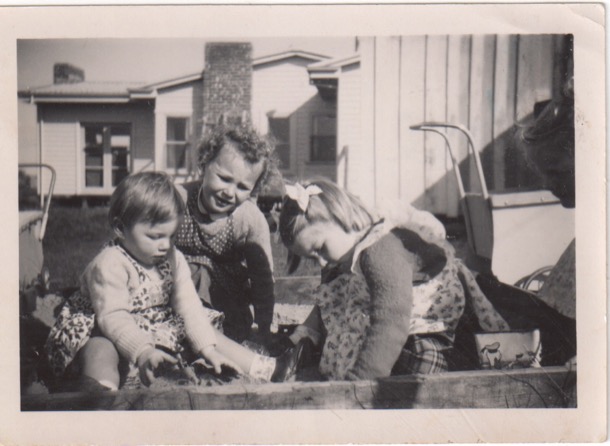

Our suburb of Box Hill South was the edge of suburbia, when our parents first bought their block. During the fifties the new suburbs filled in with more and more families, and the frontier stretched east towards the orchards of Blackburn.
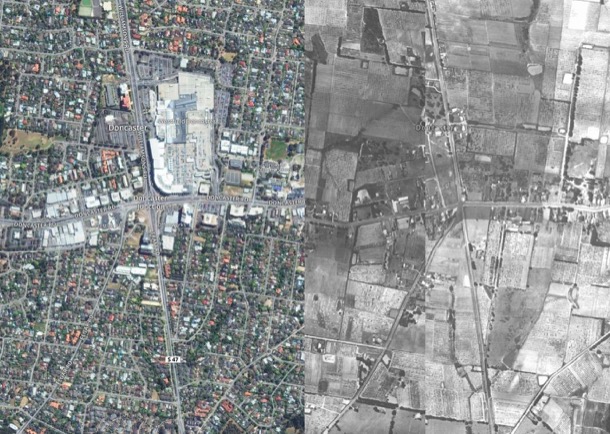
Below is Doncaster, contrasting the 1945 view to that of today. It was little changed in the 1950s. We remember breaking an axle on our Talbot car in Doncaster, a farming and orchards area with narrow unmade roads.

The sewerage reached us during the late fifties. Neighbours got together to dig each others’ trenches. The footpaths were paved, allowing us to roller-skate along them.
The streets were deemed to be safe enough for five year old girls to walk unsupervised, from Box Hill South to Surrey Hills to Sunday School and to Bennettswood to school.
We are baby boomers, and this was the most booming time. When we began school, Sue in 1954 and me in 1957, “temporary” schools were being thrown up, and unqualified teachers recruited to deal with the rush.
My first experience of school was a few weeks in “bubs”, and then the-bursting-at-the-seams class was reduced by a handful of us being put straight into Grade 1. Here is that grade photo with Miss Meadows and her 47 pupils.

1960s
This decade covers our teenage years. It was a time of huge change in the western world. By the end of the decade, Neil Armstrong had walked on the moon, women were controlling their own fertility with the Pill and popular culture had discovered the huge Baby Boomer teens market. During the sixties, there was a general loosening and questioning of traditional social norms. Older people were probably more aware of these momentous changes. For us the loosening of the cultural apron strings, that is such a feature of these times, coincided with the loosening of our familial apron strings.
The conflict between our generation’s straining at the bit and society’s entrenched traditional values played out in our school life. As fashion hemlines rose, school uniform strictures fought them. We knelt to have the gap between our uniforms and the floor measured precisely, and hastily pulled down our hoiked up dresses whenever a teacher came in sight. The anti war slogans on our pencil cases, alongside the names of pop groups we fancied, had to be kept hidden, or there would be detention. A new rule dividing the grassed hill area into a boys’ side and a girls’ side transformed the hill into a vast empty space with a cramped central area where everybody sat alongside the invisible line. In our school, as far as we can remember, there were no brown faces, hardly any Asian faces and no Aborigines. Foreigners were the Italian and Greek “new Australians”, and even they were rare in our (then) outer Eastern suburb.
Culturally, as more and more families spent more and more time around the television set, American culture rather than English, began to dominate our life.
We can’t remember exactly when we got a television set, just that it was bought specifically for watching cricket. As a family we watched the Australian serial Bellbird, which preceded the seven o'clock news. There were a succession of American sit coms we all watched, like My Favourite Martian, Bewitched, Father Knows Best, the Donna Reed show, Bachelor Father, My Three Sons and Mr Ed. After school I remember Clutch Cargo, Sea Hunt, George Reeves in Superman, and Hogan’s Heroes, F troop and Bonanza. And very rarely we were granted permission to watch 77 Sunset Strip. These are nearly all American titles. There were Australian and English shows too, but it is the American ones we remember.

With this American influence in our lives, and increasing prosperity, “teenagers”, a term first heard in the 1950s, emerged even more as a marketing target. For the first time, teenagers had their own music, fashion, language. I was more plugged into Teen culture than Sue. I began to go to local Saturday night church dances from about aged 14. There was always a live band who played rock and roll covers. A group of us from church would go.

Dress was quite formal, ties for boys and stockings and heels for girls. I remember the winter that plain coloured wool dresses with white crocheted collars and cuffs were all the rage: probably 1965. Auntie Bert, dressmaker to the wealthy ladies of Melbourne, made me a tailored aqua one with little kick pleats around the bottom.
Below is fourteen year old Margaret in the aqua wooden dress with while crocheted collar and cuffs.

During the 1960s, Australians were entrenched in the divisive Vietnam war. Our family was by default anti war, and the “all the way with LBJ” policy of our government was fiercely criticised. In 1967, my boyfriend and another close family friend was conscripted for military service. Against huge opposition, the government had voted to call up into military service some twenty year old men. Many of them ended up fighting in the jungles of Vietnam. Our mother testified in court for the other friend, who was a registered conscientious objector. But many other friends and acquaintances went off to Vietnam with their hair shaved and very basic training. Some of those veterans live with the trauma of those experiences even today.
A "Save Our Sons" movement protested against conscription:
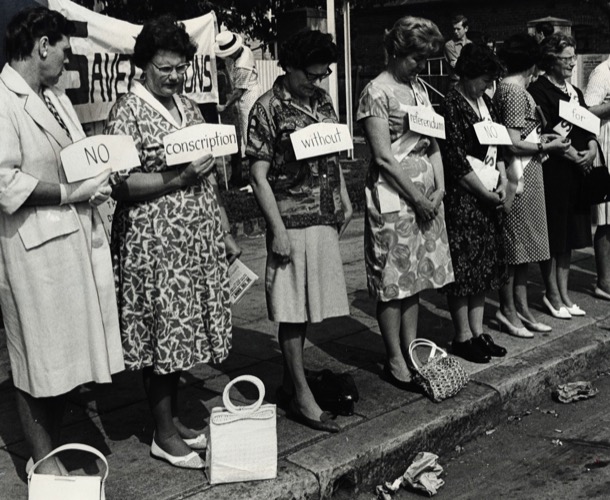

Gradually, public opinion in Australia, as in America, swung firmly against the war; and ordinary Australians demonstrated in the street.
By 1970, Sue and I had left school and were engaged in our tertiary studies, sharing a house in North Balwyn. University was still expensive, and we both managed it by gaining a bonded scholarship called a Studentship, which paid our fees, as well as a small living allowance. Even in a relatively enlightened family like ours, it was made clear that any family budget that was to be spent on university studies, was to be saved for our younger brothers, because they were boys.
1970s
The 1970s was a decade of change for us personally, and a tumultuous time worldwide. In some ways, the decade was a continuation of the 1960s. Women, gays and lesbians and other marginalised people continued their fight for equality, and many Australians joined the world wide protest against the ongoing war in Vietnam. Outrage at the continuing conflict was fuelled by the graphic coverage of the brutality of war, available nightly on our TV screens.
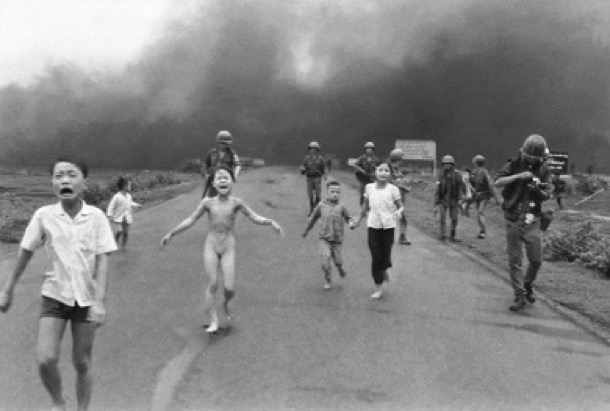

Protest was bitter and violent.

By 1975 Saigon had fallen: a humiliating defeat for the USA.
There was more violence as Pol Pot and the Khmer Rouge murdered 1.7 million Cambodians, and on the other side of the world, the IRA fought for British withdrawal from Northern Ireland.
Rapid advances in technology were in play, changing our world and planting the seeds for the creation of digital world, we are grappling with today. Apple launched the Apple 1, a desk top computer, pocket calculators were commercially available for the first time, and music became mobile with the release of the Sony Walkman.

In the popular music scene, Elvis Presley died, the Beatles split up, the Sex Pistols band recorded an album and disco music took the world by storm.
In Australia, at the beginning of the decade, Gough Whitlam led the Labour Party to victory in the 1972 election. This ended twenty-three years of unbroken Liberal-Country Party Coalition government.

Change was inevitable and rapid: the troops were brought home from Vietnam; educational reforms were introduced, such as free University education; and Whitlam visited the feared red menace, Communist China. Inept financial management, scandal and the rate of change contributed to another landmark event now known as, The Dismissal. Whitlam was sacked by Kerr, then Governor General.
Gough Whitlam stood on the steps of Parliament House and declared “Well may we say ‘God save the Queen’, because nothing will save the Governor- General”:
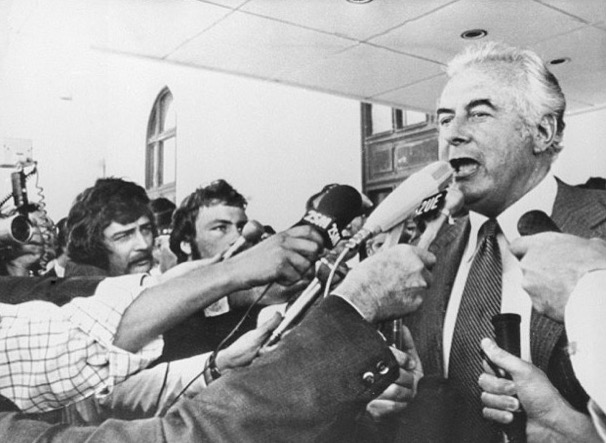

The Liberals returned to power under Malcolm Fraser. For Labour supporters like us, it was a bitter pill.
Waiting in the wings was Bob Hawke, who was both President of the ACTU and President of the Labour Party. The 1970s ended with Hawke deciding to enter politics. He was elected as the member for Wills in the 1980 election and Labour was once again in power. The 1980s in Australia was Hawke’s and Paul Keating’s decade. The reforms they ushered in changed the face of Australia: we thought for the better.
At the beginning of this tumultuous decade Margaret and I were fancy free. We moved out of home, sharing a house and living on our teaching studentships, as university education was not yet free. Margaret supplemented her income, paid $1 an hour, working at the first fast food outlet in Bourke Street. Working the late shift posed no danger as the Derby closed about 11 pm [very late] and Margaret was able to walk out to her Morris Minor parked right outside the restaurant. “It was always easy to park in Bourke Street, there were lots of parking spots,” remembers Margaret. It was such a different city then. We also embarked on our teaching careers. I began my teaching career in Sale and Margaret at Moe.
We had wonderful camping holidays, often in the Snowy Mountains; we saw interesting alternative movies at the Walhalla picture theatre in Richmond; we went to Sydney on the train to see Hair and saw nudity on stage; so risque! We listened to the Beatles, The Seekers, Cat Stevens and Peter Paul and Mary amongst others, on vinyl of course.
Margaret had begun teaching at Moe in 1973 and Jono and I, after a year overseas, both taught at Drouin High School, quite nearby. By the end of the decade, I had given up teaching and was at home at Gowar Avenue with a three year old Anna. Margaret was teaching at Croydon and was living in Gully Crescent with Ken.
Conclusion.
Marge and Alice finished their oral family history with their weddings and the end of the Second World War. It was neat: 1850-1950. It left off when they were both about thirty, settled into the business of raising children.
We are finishing our own overview at the corresponding stage. For us, this is 1980.
In the very last minute of the recording Alice, by herself for this part of the process, reflects on the speed of technological change that she and Marge had witnessed in their lifetime.
“But there’s a sort of corresponding suddenness in those new technologies and we tremble, as we think you do too, at what the outcome of all this is going to be for your children.
So looking back over that hundred years, we see this period of rapid, strong and significant development: a development that began gently enough, but now, in 1990, is rushed and killing and devastating.
And we look forward into the future for you and for our grandchildren as a time where perhaps you will learn what de-development is all about, and maybe the graph is going to go gently and firmly and calmly for you, into a period that is not as frantic as the one we’ve lived in.”
Strikingly and shockingly, the suddenness and the devastation she speaks of in 1990 has not diminished, but increased. And now, in 2018, as we watch our own grandchildren navigating their way into the world, we too tremble at what the outcome of “all this” will be.
Here is the audio of this from the recordings:
With our more modern education, we have less of a firm grasp of History, and we know that our children, and their children have, and will have, an even sparser knowledge. So we have taken the overview concept, explained a little more fully, and added in our father’s family history and other aspects we have recently discovered.
Alice and Marge finished recounting their family stories at 1950. One of our tasks in this project has been to continue on from then, and so we have done just that. We explore the nineteen fifties, sixties and seventies, linking what was happening in the wider world into our own lives.
1850-1950
Between 1839 and 1872 our ancestors arrived in Australia.They came from both Northern and Southern Ireland, England, Germany and Denmark. All were from humble origins, having worked as agricultural labourers, domestic servants, a baker and an engineer. Some were already married and others met here.
As our ancestors built their new lives in Victoria, the First Australians had already felt the disastrous impact of European contact. There had been violent conflict, the Wurundjeri population had been decimated and the survivors relocated to reserves or camps a ‘suitable' distance away from the growing population of Melbourne and outlying settlements. In 1844, when the Bourkes took up their selection at Pakenham, they were the first white settlers in the area and the “blacks camp” by the river was noted in Catherine’s memoir. Several years later, Adam Rye, from the other side of the family, was robbed by a party of ’50 blacks’. The newspaper report notes that ‘the blacks at this time were very treacherous’.
With the discovery of gold, in New South Wales and Victoria, there was a huge increase in population and in wealth.
Victoria benefitted the most. Melbourne became Australia’s largest city, with a huge land boom. Grand old buildings like the Melbourne town hall and exhibition buildings are reminders of those glory days.

The increase in population, rapid development and the attraction of the goldfields led to a shortage of workers. This meant great job opportunities at every level. It also put workers in a good bargaining position.Trade Unions developed and working conditions were the best in the world. Australia was an egalitarian workers’ paradise.
Small businessmen, like publicans, bakers and lawyers, prospered with the growth in Melbourne. For farmers, it meant bigger markets, more mouths to feed. The growth in country towns, better roads and railway development made life in the country less difficult.
Engineers had a lot of work, with the sudden development of infrastructure, and property developers were run off their feet. Our great, great grandfather, a young engineer from England, was building bridges in the expanding colony. While building the bridge across the Barwon River, his son was born, his birth unregistered.
Back in ‘Marvellous Melbourne’ our grandmother’s grandparents who had arrived from Belfast, were developing St Kilda: building large houses and public buildings for those who were prospering in the boom town.
On the land, our maternal ancestor Adam Rye, who had survived the attack by ’50 blacks’, settled in Geelong and worked as a farm labourer. He was later gripped by gold fever and went north to seek his fortune, only to be held up by bushrangers and lose his meagre pickings. His daughter married a German immigrant, Dau, and they settled on a mixed farm at Wandong. Here they raised seventeen children and supplied food to the growing population.

Meanwhile our paternal forbears, also on the land, were making their mark in Gippsland and North Central Victoria. In Pakenham the Irish Bourkes were building their family of thirteen children, and now owned Bourke’s Hotel. They were becoming significant landowners and community members, as they set about acquiring land, marrying their daughters well and establishing their sons on large and prosperous properties. They also served their community in local Government and built the horse racing industry in Pakenham.
1858 Land Sales, Michael Bourke's purchases:

The McCormacks and Hamiltons, in North Central Victoria were also acquiring and working large grazing properties, in the Goulburn Valley. They too were pillars of the local Catholic Church and community. Our grandmother was born at Balham Hill, at Molesworth, pictured below.

Melbourne became the financial centre of Australia and New Zealand. The Pakenham Bourkes’ fourth son, our great grandfather, was part of this world. He had moved to Parkville and built his law career in this thriving city. Australians were growing in confidence and the young nation was showing signs of an interest in its own identity. This was the era of Henry Lawson and Banjo Patterson, who wrote about the characters of ‘the bush’. At the same time, Tom Roberts and his paintings glorified the unique Australian landscape and the men and women who toiled there. This growing sense of identity and of nationhood is reflected in the moves for independence from Great Britain. During this era of optimism and hope our grandparents were small children, and their families were well established in both country Victoria and Melbourne.
Federation was achieved in 1901, and the country celebrated:

Australia was longer a colony but an independent nation. Melbourne was the largest city in Australia at the time and the second largest city in the Empire (after London). It was fitting that the new Parliament should sit in Melbourne while Canberra was being constructed.
The decade after Federation saw Australian women join the battle for women’s suffrage. White men over 18 in Victoria had had the right to vote since 1858, but women were not granted this right until 1908. Our maternal grandmother, Alfreda, was sixteen when women were granted the right to vote. We imagine she would have approved. She had been engaged in her own battle to pursue her dream of further education; and during this decade she finished her secondary education at Melbourne’s Continuation School, the opening of which marked the beginning of state secondary education in Victoria.
This period of prosperity, optimism, and political and social change ended in the devastation of the Word War 1. We know little of the family’s war service, but three of our maternal grandfather’s uncles served in France, and one lost his life. In the highly charged patriotic atmosphere of the time, and with mounting casualty lists, the war years must have been a difficult time, especially for our grandfather who was considered unfit for service due to ill health. He was deeply upset when given a white feather. Presumably our paternal grandfather being a country doctor, was in a protected occupation.
Our grandparents were all married at the end of this war. Our father’s parents were married in St Patricks Cathedral in a grand affair. Grace and Hugh then settled in Koroit in the Western District, where Hugh was the local doctor.

In contrast our mother’s parents were married in the Methodist Church in Surrey Hills in a small and simple ceremony where the bride did not even wear a wedding dress. At that time Alfreda was working as a teacher and Alf was working in a hardware shop in the city. They also moved to the country, soon after: to Eildon, where hardware supplies were needed for the construction of Eildon Weir.
Our family then lived through the Great Depression of the thirties, formative years for our parents who were by then at school. Our father was boarding at Xavier College and our mother was at Croydon Primary School. By the end of the decade the world was at war again.
During the war in a munitions factory, in Maribyrnong, two very different family histories were to merge into one. One was Irish Catholic, successful and quite wealthy, and the other was staunchly Protestant and relatively poor. One was involved in the Melbourne horse racing scene and the other was teetotal and interested in ideas and the new ‘isms’ that were emerging on the other side of the world. Our parents were married at the end of World War 2.
1950s
Our mother’s view of the 1950s, in her recording, is of a time of burgeoning economic growth and development. To us, it is the decade we first became aware of the world.
Our world was redolent with Australiana, but we were intensely aware of our British heritage, and it dominated our reading, our schooling, our whole culture. A portrait of The Queen hung in our school. Sue remembers keeping a scrap book at home of magazine articles about the Royal Family. She was particularly interested in the corgis. Apparently I had one too, and it contained very many pieces about Princess Margaret.
Enid Blyton Books:

Globally, it was a dangerous world, with the cold war in full swing, and a very real threat of nuclear war. Our parents had quite well developed political opinions, particularly our mother, so we were exposed to adult conversations about the issues of the day. Family friends and neighbours, the Lees, were active in the union movement. They encouraged our parents’ involvement in the movement for “unilateral disarmament” and other left wing activities. I remember our mother’s admiration for an older couple who took a small boat out into the Pacific Ocean to protest the nuclear testing. Bikini Atoll in the Pacific, sixty years on, is still a no go zone from the USA nuclear tests carried out there up until 1958.

This was the time of McCarthyism in America, and Australian political attempts to ban the Australian Communist Party: a divisive time, where everyday people had strong opinions one way or the other. Sue remembers Prime Minister Menzies as “the devil incarnate”.
The Campaign for Nuclear Disarmament became overwhelmed in the 1960s by anti Vietnam War action, but it was an important political movement of the 1950s. The familiar “Ban the Bomb”, or “Peace” symbol was invented in 1958, as a symbolic representation of ND (Nuclear Disarmament)

Our family was, by today’s standards, quite poor, but this did not impinge on our life, at this time. We were well fed, we had a stay at home mother who looked after us and the struggle to pay bills was not part of our conscious experience. As far as we children knew, we were neither poorer nor better off than our neighbours, with the exception of the family in the housing commission house nearby, whose son had polio and who didn’t always have enough to eat. The world, as we observed it in our daily life, was largely classless. Perhaps Australia at this time really was the egalitarian workers’ paradise it purported to be, to prospective migrants in Britain. (only whites of course)
Nevertheless, we knew about the religious and economic differences within our family: that our father’s relatives were wealthy and that we were not, because our parents’ union was a “mixed marriage” and very disapproved of. We were very aware of their Catholicism and our Protestantism, and that we were not as close to our grandmother as our cousins were.
Our father during the 1950s, went from working as an industrial chemist by day, and studying by night, to full time teaching. We got our first car, a television and a refrigerator. By the end of the decade there had been four children born. It was busy, but simple life, encumbered by very little “stuff”.

Our suburb of Box Hill South was the edge of suburbia, when our parents first bought their block. During the fifties the new suburbs filled in with more and more families, and the frontier stretched east towards the orchards of Blackburn.
Below is Doncaster, contrasting the 1945 view to that of today. It was little changed in the 1950s. We remember breaking an axle on our Talbot car in Doncaster, a farming and orchards area with narrow unmade roads.

The sewerage reached us during the late fifties. Neighbours got together to dig each others’ trenches. The footpaths were paved, allowing us to roller-skate along them.
The streets were deemed to be safe enough for five year old girls to walk unsupervised, from Box Hill South to Surrey Hills to Sunday School and to Bennettswood to school.
We are baby boomers, and this was the most booming time. When we began school, Sue in 1954 and me in 1957, “temporary” schools were being thrown up, and unqualified teachers recruited to deal with the rush.
My first experience of school was a few weeks in “bubs”, and then the-bursting-at-the-seams class was reduced by a handful of us being put straight into Grade 1. Here is that grade photo with Miss Meadows and her 47 pupils.

1960s
This decade covers our teenage years. It was a time of huge change in the western world. By the end of the decade, Neil Armstrong had walked on the moon, women were controlling their own fertility with the Pill and popular culture had discovered the huge Baby Boomer teens market. During the sixties, there was a general loosening and questioning of traditional social norms. Older people were probably more aware of these momentous changes. For us the loosening of the cultural apron strings, that is such a feature of these times, coincided with the loosening of our familial apron strings.
The conflict between our generation’s straining at the bit and society’s entrenched traditional values played out in our school life. As fashion hemlines rose, school uniform strictures fought them. We knelt to have the gap between our uniforms and the floor measured precisely, and hastily pulled down our hoiked up dresses whenever a teacher came in sight. The anti war slogans on our pencil cases, alongside the names of pop groups we fancied, had to be kept hidden, or there would be detention. A new rule dividing the grassed hill area into a boys’ side and a girls’ side transformed the hill into a vast empty space with a cramped central area where everybody sat alongside the invisible line. In our school, as far as we can remember, there were no brown faces, hardly any Asian faces and no Aborigines. Foreigners were the Italian and Greek “new Australians”, and even they were rare in our (then) outer Eastern suburb.
Culturally, as more and more families spent more and more time around the television set, American culture rather than English, began to dominate our life.
We can’t remember exactly when we got a television set, just that it was bought specifically for watching cricket. As a family we watched the Australian serial Bellbird, which preceded the seven o'clock news. There were a succession of American sit coms we all watched, like My Favourite Martian, Bewitched, Father Knows Best, the Donna Reed show, Bachelor Father, My Three Sons and Mr Ed. After school I remember Clutch Cargo, Sea Hunt, George Reeves in Superman, and Hogan’s Heroes, F troop and Bonanza. And very rarely we were granted permission to watch 77 Sunset Strip. These are nearly all American titles. There were Australian and English shows too, but it is the American ones we remember.

With this American influence in our lives, and increasing prosperity, “teenagers”, a term first heard in the 1950s, emerged even more as a marketing target. For the first time, teenagers had their own music, fashion, language. I was more plugged into Teen culture than Sue. I began to go to local Saturday night church dances from about aged 14. There was always a live band who played rock and roll covers. A group of us from church would go.

Dress was quite formal, ties for boys and stockings and heels for girls. I remember the winter that plain coloured wool dresses with white crocheted collars and cuffs were all the rage: probably 1965. Auntie Bert, dressmaker to the wealthy ladies of Melbourne, made me a tailored aqua one with little kick pleats around the bottom.
Below is fourteen year old Margaret in the aqua wooden dress with while crocheted collar and cuffs.

During the 1960s, Australians were entrenched in the divisive Vietnam war. Our family was by default anti war, and the “all the way with LBJ” policy of our government was fiercely criticised. In 1967, my boyfriend and another close family friend was conscripted for military service. Against huge opposition, the government had voted to call up into military service some twenty year old men. Many of them ended up fighting in the jungles of Vietnam. Our mother testified in court for the other friend, who was a registered conscientious objector. But many other friends and acquaintances went off to Vietnam with their hair shaved and very basic training. Some of those veterans live with the trauma of those experiences even today.
A "Save Our Sons" movement protested against conscription:

Gradually, public opinion in Australia, as in America, swung firmly against the war; and ordinary Australians demonstrated in the street.
By 1970, Sue and I had left school and were engaged in our tertiary studies, sharing a house in North Balwyn. University was still expensive, and we both managed it by gaining a bonded scholarship called a Studentship, which paid our fees, as well as a small living allowance. Even in a relatively enlightened family like ours, it was made clear that any family budget that was to be spent on university studies, was to be saved for our younger brothers, because they were boys.
1970s
The 1970s was a decade of change for us personally, and a tumultuous time worldwide. In some ways, the decade was a continuation of the 1960s. Women, gays and lesbians and other marginalised people continued their fight for equality, and many Australians joined the world wide protest against the ongoing war in Vietnam. Outrage at the continuing conflict was fuelled by the graphic coverage of the brutality of war, available nightly on our TV screens.

Protest was bitter and violent.

By 1975 Saigon had fallen: a humiliating defeat for the USA.
There was more violence as Pol Pot and the Khmer Rouge murdered 1.7 million Cambodians, and on the other side of the world, the IRA fought for British withdrawal from Northern Ireland.
Rapid advances in technology were in play, changing our world and planting the seeds for the creation of digital world, we are grappling with today. Apple launched the Apple 1, a desk top computer, pocket calculators were commercially available for the first time, and music became mobile with the release of the Sony Walkman.

In the popular music scene, Elvis Presley died, the Beatles split up, the Sex Pistols band recorded an album and disco music took the world by storm.
In Australia, at the beginning of the decade, Gough Whitlam led the Labour Party to victory in the 1972 election. This ended twenty-three years of unbroken Liberal-Country Party Coalition government.

Change was inevitable and rapid: the troops were brought home from Vietnam; educational reforms were introduced, such as free University education; and Whitlam visited the feared red menace, Communist China. Inept financial management, scandal and the rate of change contributed to another landmark event now known as, The Dismissal. Whitlam was sacked by Kerr, then Governor General.
Gough Whitlam stood on the steps of Parliament House and declared “Well may we say ‘God save the Queen’, because nothing will save the Governor- General”:

The Liberals returned to power under Malcolm Fraser. For Labour supporters like us, it was a bitter pill.
Waiting in the wings was Bob Hawke, who was both President of the ACTU and President of the Labour Party. The 1970s ended with Hawke deciding to enter politics. He was elected as the member for Wills in the 1980 election and Labour was once again in power. The 1980s in Australia was Hawke’s and Paul Keating’s decade. The reforms they ushered in changed the face of Australia: we thought for the better.
At the beginning of this tumultuous decade Margaret and I were fancy free. We moved out of home, sharing a house and living on our teaching studentships, as university education was not yet free. Margaret supplemented her income, paid $1 an hour, working at the first fast food outlet in Bourke Street. Working the late shift posed no danger as the Derby closed about 11 pm [very late] and Margaret was able to walk out to her Morris Minor parked right outside the restaurant. “It was always easy to park in Bourke Street, there were lots of parking spots,” remembers Margaret. It was such a different city then. We also embarked on our teaching careers. I began my teaching career in Sale and Margaret at Moe.
We had wonderful camping holidays, often in the Snowy Mountains; we saw interesting alternative movies at the Walhalla picture theatre in Richmond; we went to Sydney on the train to see Hair and saw nudity on stage; so risque! We listened to the Beatles, The Seekers, Cat Stevens and Peter Paul and Mary amongst others, on vinyl of course.
Margaret had begun teaching at Moe in 1973 and Jono and I, after a year overseas, both taught at Drouin High School, quite nearby. By the end of the decade, I had given up teaching and was at home at Gowar Avenue with a three year old Anna. Margaret was teaching at Croydon and was living in Gully Crescent with Ken.
Conclusion.
Marge and Alice finished their oral family history with their weddings and the end of the Second World War. It was neat: 1850-1950. It left off when they were both about thirty, settled into the business of raising children.
We are finishing our own overview at the corresponding stage. For us, this is 1980.
In the very last minute of the recording Alice, by herself for this part of the process, reflects on the speed of technological change that she and Marge had witnessed in their lifetime.
“But there’s a sort of corresponding suddenness in those new technologies and we tremble, as we think you do too, at what the outcome of all this is going to be for your children.
So looking back over that hundred years, we see this period of rapid, strong and significant development: a development that began gently enough, but now, in 1990, is rushed and killing and devastating.
And we look forward into the future for you and for our grandchildren as a time where perhaps you will learn what de-development is all about, and maybe the graph is going to go gently and firmly and calmly for you, into a period that is not as frantic as the one we’ve lived in.”
Strikingly and shockingly, the suddenness and the devastation she speaks of in 1990 has not diminished, but increased. And now, in 2018, as we watch our own grandchildren navigating their way into the world, we too tremble at what the outcome of “all this” will be.
Twenty-Eight Moore Street
13 07 16 15:47 Filed in: Children 1950s
Alice describes the acquisition of the land in Box Hill South in 1946:
Dad built the house over the following six years, while studying night school and working full time at the gasworks in Box Hill. Sue remembers going to the Moore Street site, Dad walking and she riding her trike. On one memorable occasion, on the corner of Broughton Road and Elgar Road she remembers waiting while a circus went past: wild animals in cages and horse drawn vehicles.
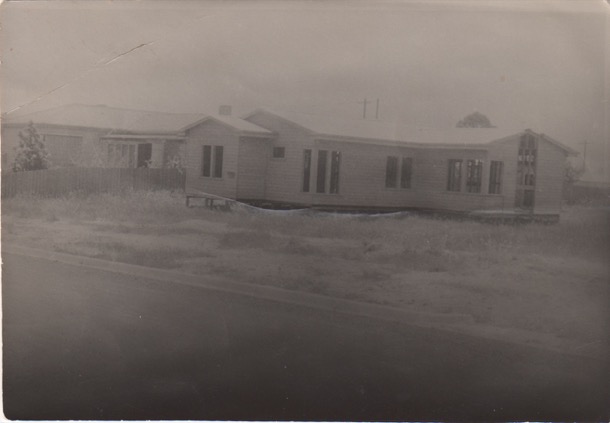

Neither Sue nor I remember the move from Boronia St, but it must have been in 1952. The house was never actually finished. The back door remained the one Dad had knocked up to lock up the house. We four kids all lived there until we were in our late teens or early twenties and our mother remained living in in the Moore St house until she was in her fifties.
The house is still there. It had a view over Mt Dandenong, and was pretty much on the edge of suburban development. Beyond, further east were orchards, unmade roads and “the country”.
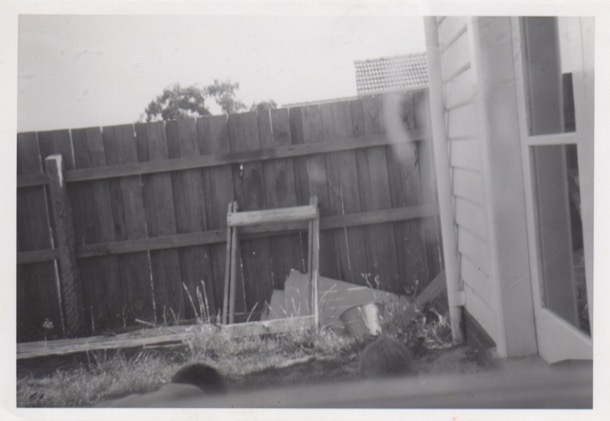

Outside was a garden, overlooked by a grass terrace, which had French windows opening onto it. Later this terrace area became a “rumpus room” when our grandparents built a flat onto the back of the house in about 1960.
Right down the back was a vegetable garden and chook pen. Sue remembers hanging on the fence eating an apple, and looking into the paddock next door.
The driveway led through full height double wooden doors into the garage. I remember the garage full of shelves of smelly, dark looking tools, piles of sawn timber and car bits. Our first car was a Talbot, huge and square. it was cream with red leather

Later it was replaced with a Sunbeam. I remember being confused about the Sunday School song “Jesus wants me for a sunbeam”, but lots about life made little sense. This was just one other enigma.
Attached to the side of the garage was a garden tap, and at the end, a swing.
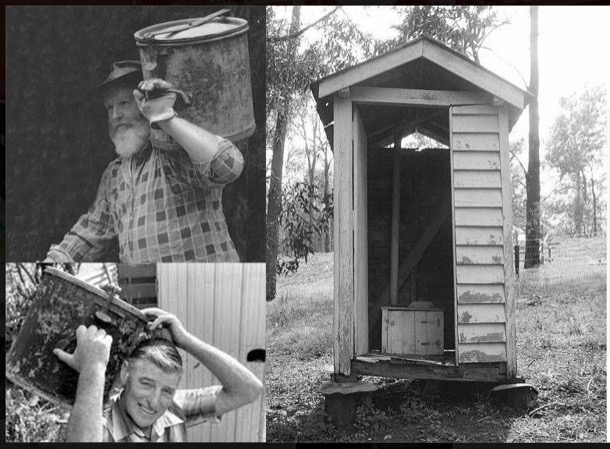
Part of the garage building was the alcove for the outside toilet, which we used until the sewerage came through. The toilet consisted of a can with a shelf above it, with the seat built into the shelf. At night we used the potty instead. Our bedtime instructions were “potty, teeth and bed”. The "can" was collected every week by the "dunny man".

Moore Street House Room by Room
The Girls’ Bedroom.
Sue and I shared the front room of the house. Initially, the room was a pale dusky pink coupled with a pastel greeny aqua. Later this was changed soft grey with navy and red curtains, replacing the white venetian blinds, and navy blue bedspreads. Sue remembers buying the fabric for the curtains and bedspreads, with Auntie Marge as style consultant, from a shop in Richmond.
Dad built double bunks, offset, with drawers under the upper one, and a plywood dressing table opposite the bunks and long desk under the front window. Sue remembers working on that desk as an older student.
We wore cotton nighties all year through. Sue slept in the lower bunk, and I the upper one. Above my bed was a high window. I remember standing on my bed watching an occasional visitor walking down the driveway below. On cracker nights, after all the neighbourhood kids were back home in bed, the window also afforded a view of Gilbert Soames, the older, strange boy next door, letting off his own crackers, all by himself, in front of his house.
We went to bed at the same time, in spite of the three year age gap. We would read until lights out, (and sometimes afterwards with clandestine torches or a candle). We also talked in the dark. A favourite game after lights out was to take it in turns to relate “everything I did today from waking up until now”. This would often mean a droning voice going on long after the other one had dropped off to sleep.
In Spring the pittosporum in front of the room filled the air with its sweet blossom.
Around dawn there would be the sound of the milkman’s horse clip clopping along the street.
During one of the evenings leading up to Christmas a small brass band from the Salvos might stand on the street corner and play carols, before marching off to the next street. On Christmas morning there would be a satisfying lump of filled pillowslip on the end of each bed.
Clothes storage was in a singe wardrobe, the drawers under the upper bunk, and shelves in another cupboard.
We had very few toys, a few dolls and books mostly. These lived on two, usually messy shelves in the cupboard. There was always a pile of cartridge paper for drawings, on one side of which was Dad’s students’ mechanical drawing school work. We don’t remember playing in our bedroom, in fact really only reading, lying on our beds.
The sheets were changed once a week. The top sheet would be put on the the bottom, (there were no fitted sheets) and the bottom sheet and pillow slip would be changed.
An overwhelming memory is of hot nights. The room faced west and there was no insulation, let alone air conditioning! Sometimes Mum would bring us each a wet face washer to put on our forehead, but it soon became warm again.
Getting up after we had been put to bed was frowned on. Sue remembers the dark hall that led from their bedroom as terrifying. It was a big deal to get up. I remember worrying a loose tooth until it came out, as this was a big enough excuse to tiptoe up the hall and open the door into the living area, where our parents sat and read and smoked cigarettes after the children were in bed. There were no night lights, except a friendly street light nearby. It was often frightening at night. One summer’s night, after a trip to the beach, I remember being quite certain I could hear “a man” lighting matches nearby, trying to burn the house down. The next morning, it was discovered that a bowl full of crabs in the boys room, brought home from the beach, had escaped and spread all over the house, scratching their way through cupboards and creating scary noises.
The Boys' Bedroom
Yeah, well it was a boys' bedroom.
The Bathroom
One bathroom served the family of six. The floor was black rubber, and a home made stool was covered in the same rubber.
The large pink bath had a towel rail attached to the wall above, right along its length. When more than one child was in the bath, these “fell” into the water often enough for “Mum, a towel fell in the bath!” to seem a familiar call. A shelf at the end of the bath held face washers, a few alarming medical devices and a tin of borax, for athletes foot. Sometimes there would be a bath toy such as a pop pop boat, but these were rare.
The shower recess, protected by its curtain seemed dark and a bit scary. There were no tiles, just cement sheeting, and it seemed a bit icky and threatening.
A little cupboard above the pink basin held Dad’s shaving things, the tooth brushes and toothpaste, a compact and a few very red lipsticks, which had worn into a concave pattern. Nail scissors were attached to a pink metal stand, picturing glamorous lady pictured bending over slim legs, said ”Now cut those toe nails!” There were a few rudimentary first aid items and a deodorant which was a cream in a shallow bowl with a glass lid. There were also bars of yellow velvet soap, which these days we would call laundry soap, and which were used for everything: hair, bodies, dishes, hand washing of clothes and floors. There was no vanity table. The basin stood on a pedestal, with hot water pipes covered in hessian lagging.
A long narrow room off the bathroom was built ready for when the sewerage was put on. In our early memories it holds building detritus. Later it had a toilet in it, but there was never a door.
The Parents’ Bedroom
The wooden double bed was made by Dad. Mum’s side had a bedside chest of drawers on which were books, a Bible, and a lamp. Dad’s side had a chair on which he kept similar items.
There were three built in wardrobes. One each for hanging clothes, and a middle one with shelves either side. Dad’s side smelt of leather and tobacco, and held his collection of 78 vinyl records, and his pipes. Mum’s smelt of perfume and had a very few items of jewellery and lacy underwear . The top shelf on Mum’s side was the hiding place for Christmas and birthday presents.
The Hall
A square entrance hall in our early memories is empty, except for the cupboard in which we hung our coats.
Later when we had a telephone (our number began with XY) there was a black metal monstrosity called a “telephone table” with a wooden seat and a shelf for the telephone and the jar, into which we had to put money when we used the telephone.
The Kitchen
The kitchen table at Moore St was the centre of the house and its large plywood surface saw many varied activities besides breakfast, lunch and dinner. It hosted our mother reading The Age from cover to cover and then playing Patience; (instead of doing more mundane tasks like housework) sewing all manner of things from trailer covers, curtains and summer clothes; lots of talking and even a seance or two in later years.
The walls were bright yellow and the ceiling pale blue. Large cupboards and a gas stove and oven occupied one wall and adjacent to this was a long row of cupboards topped by crowded benches and a sink where we fought over who should wash and who should wipe the bench after the job was done. (The rules were complicated! NOT, just the interpretation.)
The oven was another focal point. On top was a metal ashtray holding a few coins and used matches, a hairbrush and lots of letters and bits of paper. Margaret and I both had our hair done in front of the oven in the morning, marking our growth by the marks on the oven door.
Beside the stove was a salt cellar and an old jam tin into which the dripping was poured.
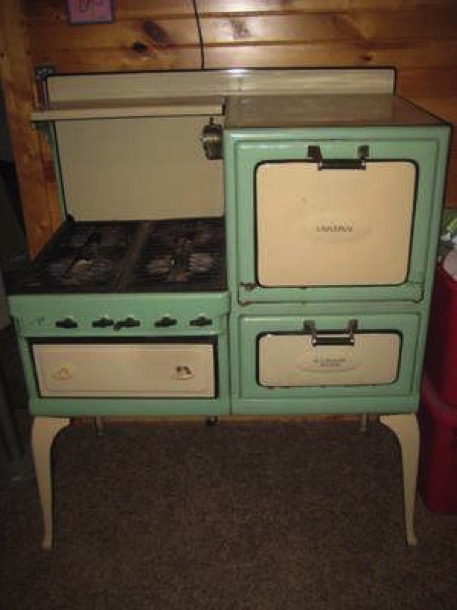

The only appliances were a Sunbeam Mixmaster and the electric frypan kept on the bench near the stove. With the pile of newspapers under the corner cupboard, the sink and our two appliances there was only a small preparation space for the busy work of school lunches and daily cooking.
Sue remembers the ice chest in which was stored a large block of ice delivered by the iceman who with a hessian bag draped over his shoulder, carried in the big block ice held in place with a large ice hook.
A grey wooden fence was about two and a half metres away, outside the kitchen window. A double row of hand laid red bricks made the driveway, with a narrow garden bed each side. Under the window were red geraniums and blue campanula climbed the fence. The Soames' garden next door had fragrant mock orange and honeysuckles trees, whose perfume would waft in on the breeze. Most nights, from a very early age, Sue and I stood at that window and washed and dried the dishes.
The Laundry.
This room seemed small, dark, crowded and vaguely threatening. It was very much a utilitarian room, made of unpainted fibre cement sheeting. There were often metal buckets of mysterious items soaking in the concrete troughs, under which was an enormous pile of newspapers: The Age which would get soaked through when one of the troughs overflowed. Above the troughs a shelf held Rinso washing powder and the iron. Early on we had a small washing machine topped by a mangel. It wasn’t until the mid nineteen-sixties that we had a modern spin drying washing machine. On the other wall of the laundry was a huge hot water tank on a stand and the briquette hot water service, on a lower shelf under which was the hessian bag of briquettes. There was a tray of apricot coloured ash to be emptied under the fire box. Behind the door, brooms and mops were kept along with the ironing board and an electric floor polisher. There was often a clothes horse of clothes and nappies, drying by the hot water service. No wonder it seemed crowded.
The Dining Room
Grandma Bourke gave us the large shiny wooden dining table and chairs. We don’t know the circumstances of this gift. Maybe it became redundant after Grandpa Bourke died in 1950, and she moved out of the large house. We ate our evening meals around this table, complete with instructions about table manners and the endless wars about eating all one’s vegetables. A barely used open fire was on one side of the room and a huge gothic sideboard on the other. Wedding presents, seldom used platters and bowls and precious cups and saucer sets were kept in the lockable cupboards, and a few on display in the glass fronted middle cupboard. There were also drawers. We remember the items that lived in this sideboard with hushed reverence. There was a set of fish knives, cake plates and cake forks, wine glasses, smoked glass dessert bowls, serviette rings, doilies and other embroidered items, “ornaments” including a china “old fashioned” lady with a blue skirt made of hardened net.
The Lounge Room
On one side, French windows opened out onto a grassed terrace. On the other, venetian-blind covered windows on two walls met in the corner of the room. There was an open fireplace, which later became a “Wonderheat”, gas heater, and a stone hearth. The early furniture in there were huge dark chairs, a cream rocker and a gramophone with its red fabric covered speaker and curly legs. An ashtray on a stand, with a box of matches perched on the side, sat beside the fireplace.
Later, in the nineteen sixties the room received a makeover and black tubular furniture with and a pair of Fleur armchairs with grey and aqua vinyl cushions took over. The television, hired initially around nineteen sixty, for a summer Ashes cricket series and watched on the dining room table from the kitchen, eventually became the focus of the lounge room. There were only five chairs. The boys sat on the floor, often engaged in vigorous play fighting, especially when World Championship Wrestling was on.
The Necessities of Life
In so many ways, as you will have realised, we grew up in a very different world. Many of the items we now automatically drive to buy in the supermarket, were delivered. The following is a very descriptive account of the daily deliveries and the weekly rubbish collection. By the way, there was one rubbish bin per household, and all rubbish was wrapped in newspaper. Wrapping the rubbish so that the contents were secure, was quite an art, as you can imagine.
“The driver moved forward about three houses at a time and the garbos ran down the street knocking the lids off the old-style galvanised iron bins. Then they hoisted the bin to their shoulders, ran back to the truck, tipped the load over the side (there were no compactors in those days), giving it a good bang on the edge to make sure all the contents were dislodged. Then they chucked the bin onto the grass verge.
It has occurred to me since that the advent of grass verges, ‘nature strips’ as they were improbably titled in the new suburbs then springing up, may have been partly to help muffle this noisy process. With all that running and hoisting, garbos had to be very fit and, unsurprisingly, many were football players. They also collected empty beer bottles (to be refilled), which they stowed in big hessian bags slung on the rear of the truck.
At Christmas it was the custom to leave the garbos a bottle of beer or three for their Christmas party. If you didn’t leave them a drink, they spilled some of your garbage on the nature strip.
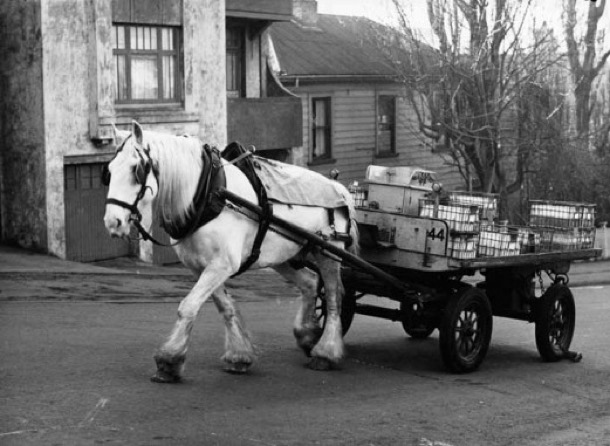
Virtually every household had milk and bread home delivered. In the mid-1950s there were still a hell of a lot of people who didn’t own a car, so there was a lot of demand for these services. There were no supermarkets providing the whole range of daily necessities, and even the electric refrigerator wasn’t yet a universal feature of homes. I can remember my parents, when I was very young, relied on an old ice chest, for which a block of ice measuring about 30 centimetres square was delivered every couple of days by the iceman.
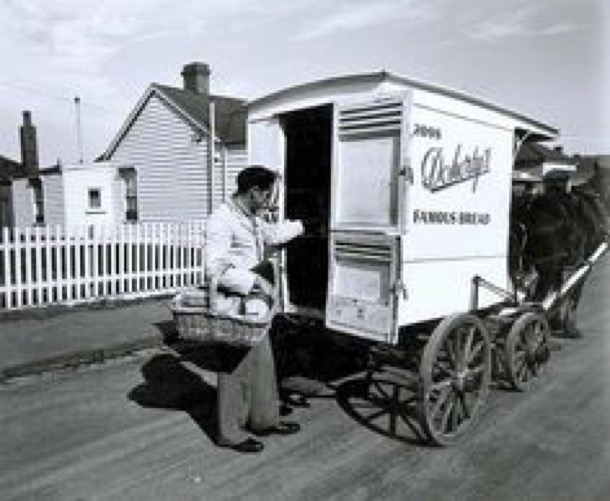
Both the milkman and the baker used horse-drawn vans. In an age when motor vehicle ownership was surging ahead, this was still a more efficient way to make deliveries than using a motor van, because there was no need to jump into and out of the driver’s seat all the time. The baker or the milko whistled to signal the horse to move on down the street. Once the horse knew the round, the deliverer didn’t even have to do that. It just ambled on to the next regular customer and waited obediently outside.

The baker trotted down the street carrying loaves in a big wicker basket slung on his arm. There were only two types of bread: ‘white’ and ‘brown’ (or what we’d call wholemeal these days). They were high-top loaves which could be broken into two halves. Some people only had half a loaf delivered each day and maybe a full one on Fridays for the weekend.”

Our mother walked to the local grocer, fruit shop and butcher once a week where the rest of the food was bought. The shopping was delivered to our house until we bought a car. From then on the shopping was collected by our father on his way home. The butcher and greengrocer were much the same as today, except that the butcher had sawdust on the floor and there was not a piece of cling wrap plastic to be seen. The grocer however was very different.
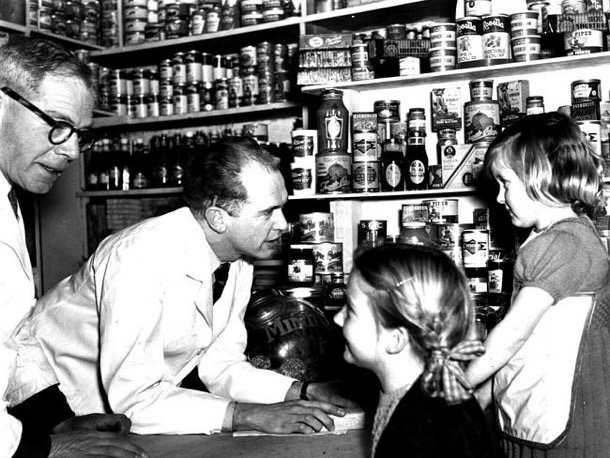

No taking pre-packaged items off the shelves. Instead, the grocer served his customers, putting all the items bought into very sustainable brown paper bags. Big tins lined some of the shelves that held such items as biscuits, broken biscuits and small items such as dried fruit. Larger bins held flour, sugar etc. The best thing about the grocer was the inexpensive treat of a small bag of broken biscuits. Soon after we moved to Box Hill South, the amazing Foodland Supermarket opened and gone were the days of personal service and bags of broken biscuits for children.


