Hair
08 02 23 13:08 Filed in: Alice
Our plan was to write about hairstyles. Many of our family photos feature the hairstyles that were popular at the time, so we spent a long time gazing at the photos. Soon we found ourselves discussing particular people: their lives, their relationships, the circumstances of particular photos.
This post therefore is about hairstyles, but we have allowed ourselves a much broader scope.
ALFRED JOHN COATES
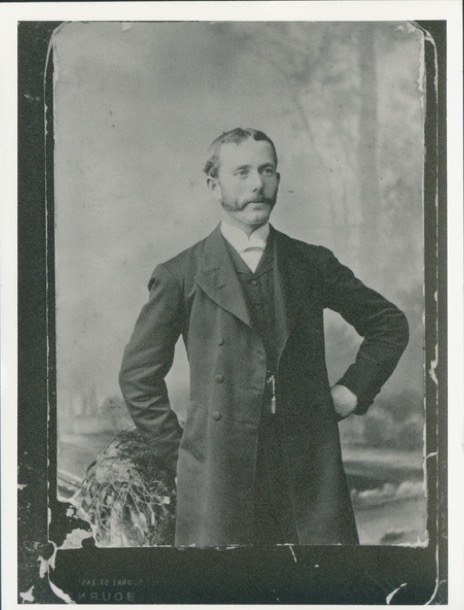

Alfred John Coates, born in 1857, was probably in his late twenties when this photo was taken. He was our maternal great grandfather and was a Methodist Pastor for most of his working life. In this photograph Alfred is a young man in prime of life, dressed in formal dress and sporting the fashion of the day: mutton chop whiskers, carefully manicured to join artfully with the moustache. A man of destiny, the misty ‘bush’ behind him, he stands erect, eyes on the future. At this time Alfred was apparently a boiler maker in Ballarat.
Men’s facial hair trends were changing rapidly in the late 1800s. Long beards were out and clean chins and cheeks and a well-manicured moustache were in. To achieve this look men would need to go to a barber two to three times a week or shave themselves.

Shaving oneself may have been a financial necessity at times but it could also be a dangerous procedure. Shaving was done with a straight steel razor that required care and expertise, not only in the act of shaving the gentleman, but also in the care of the blade. To keep it sharp, the blade was rubbed against a leather or canvas strap before each new shave. As well as the blade, shaving soap, shaving brushes, combs, oils and wax were essential items to achieve the desired effect.
Having a photograph taken in a studio was a special occasion and a relatively expensive exercise. One can imagine that Alfred may have had a trip to the barber to ensure that he looked his best.

Safety steel razor blades that made shaving much easier were not invented until 1895 by an American business man with French heritage.
King C. Gillette invented a low cost blade that was easily replaceable and gave men safety and the freedom to achieve the look desired themselves.
EMMA ELIZABETH DAU
Alfred married Emma Elizabeth Dau in 1888. He was thirty-two and she was twenty Maybe this photo was taken at this time:

Emma is dressed in the style of the day, hourglass figure no doubt with a corseted waist as she gazes into her future with a determined tilt of her chin. Her hair is tightly curled at the front and pulled back into either a bun or pinned up plait.
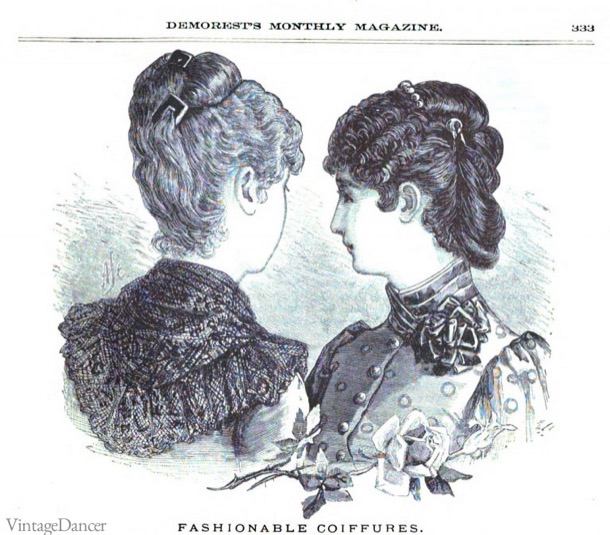

Unlike the men who had barbers to attend to their needs, there don’t appear to be many ladies' hairdressers. Women had many home implements and potions and maybe sisters and mothers helped each other with their hair.
Young Emma’s tight curls may have been created with curling irons. A curling iron consisted of a metal rod that was held over a flame or burning alcohol to heat it, before wrapping the hair around it. Hey presto, curls!
Later in life, Emma wore her hair in a more relaxed style, loosely pulled back from her face and pinned up into a bun at the back:
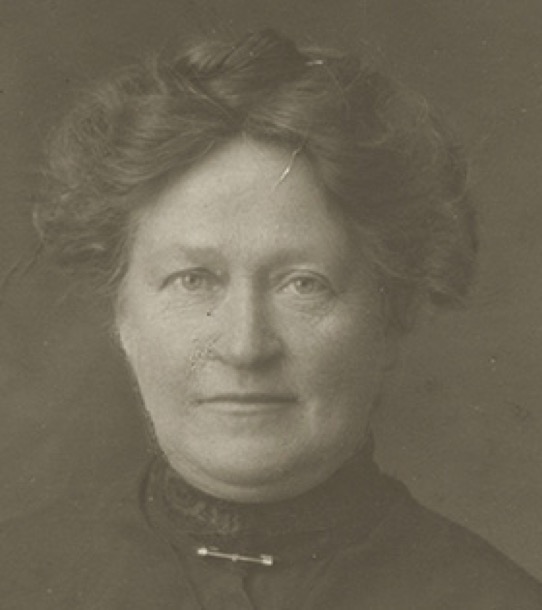

When this photo was taken, the height of fashion for women was to wear their hair with more volume at the sides. This was created by using clumps of hair leftover in combs and brushes, to pad out the sides. Emma would not have gone to these lengths in later life, but on her dressing table she would have had a brush, comb, hand mirror and china box, with a lid for the collection of hair caught in brushes or combs. We can remember our grandmother, Alfreda, also having these items on her dressing table. She wore her hair long all her life. During the day it was loosely tied back in a bun, brushed out at night, and the ‘ratts’ collected from the brush and placed in the china box. She then plaited her hair into a loose, single long plait and was ready for bed.
NINE DAU SISTERS
Emma Coates, was born Emma Dau. She was one of seventeen. The first nine of these were girls.
We have three amazing little photos of some of the Dau children. We have spent a long time staring at these images, noticing little details, wondering about the lives of these nine little girls.
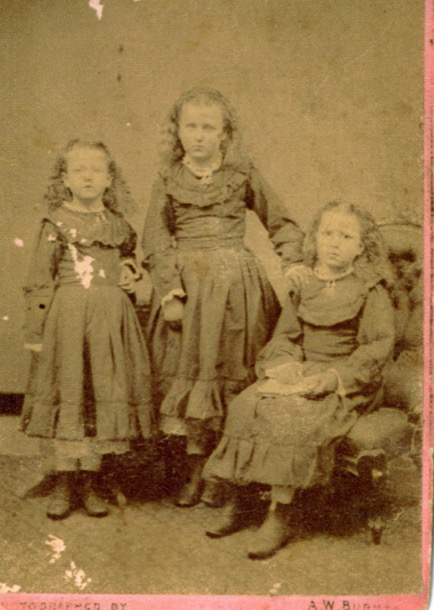
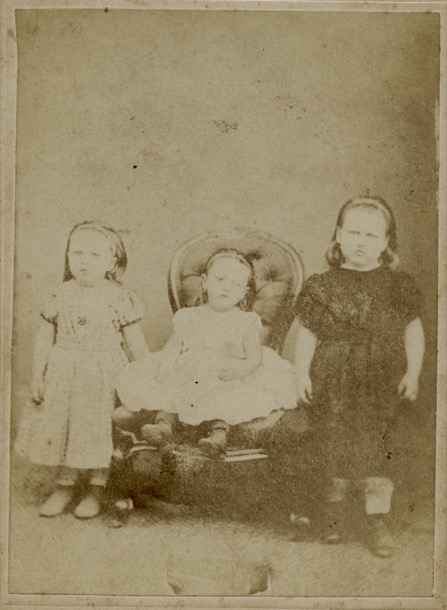



The first question we had was, "Were the three photos taken at the same time?". There is such a family resemblance, we weren’t sure at first whether they were different people in the three photos. The carpet gives away that they were taken in the same studio. On the back of one of the playing card sized photos, we see “one shilling per copy”. For context, at that time, a shilling was more than a day’s wage for a working man.
It seems most likely that the three photos were taken on the same day, and they are the nine oldest children, all daughters, of Joachim and Martha Dau, our great, great grandparents.
The photo of the three eldest has writing on the back:

The fact that Martha is misspelt as “marther”, and that no capital letters are used, might be a clue. It was not our mother Alice, nor her parents. None of them would have made such a basic spelling error! The surname is listed as “Dow”.
If those names are correct, then these are the three eldest Dau children. Standing is Sarah, the eldest. the other two are Martha, known as Mishi, and Emma, our great grandmother.
Thanks to the Wandong Historical group, we have the details of nearly all the Dau children.
The next three girls are Bella, Jane and Sophia, followed by Alice, and two others, possibly Annie and Nance, although some sources have Annie and Nance as the same person.
There is no date on these photos, but there are nine girls. The nine first Dau children, all girls were born between 1866 and about 1878. This puts the date of the photos at about 1880, with Sarah, the eldest, aged 14 and the youngest aged 2.
The girls’ father, Joachim, had spelt his surname, Dau. We don’t know the exact date they changed it to Dow, but Frederick enlisted to fight in the Boer War as Dow in 1901, and Arthur, who became a professional soldier, changed his name by deed poll to Dow. The same anti German sentiment that caused the British Royals to change their surname to Windsor from Saax Coburg was no doubt responsible. And yet the Dau spelling persists alongside the Dow spelling, right up until 1929, when Sarah, the eldest wrote about her childhood. Our mother and aunt did not even know about the Dau spelling.
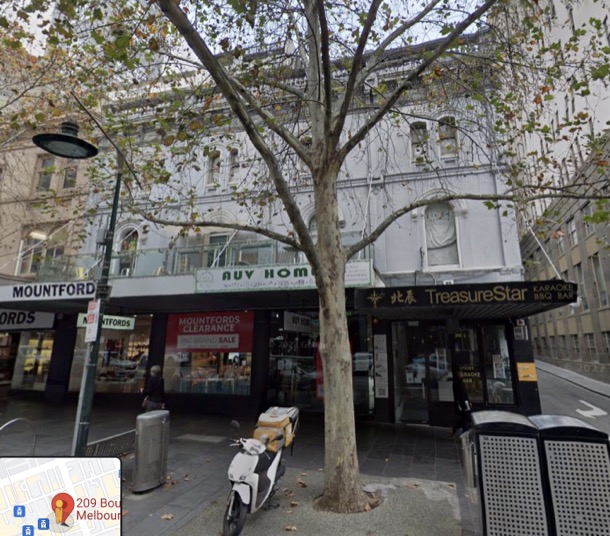
The photographer is listed on the back as Burman, 209 Bourke St Melbourne. The building is still there. This is what it looks like today:

There are a number of old photos by Burman available on line, with that tell-tale carpet visible in some. This one, “Portrait of a Lady”, which uses the same chair as two of our photos, is from C1865.

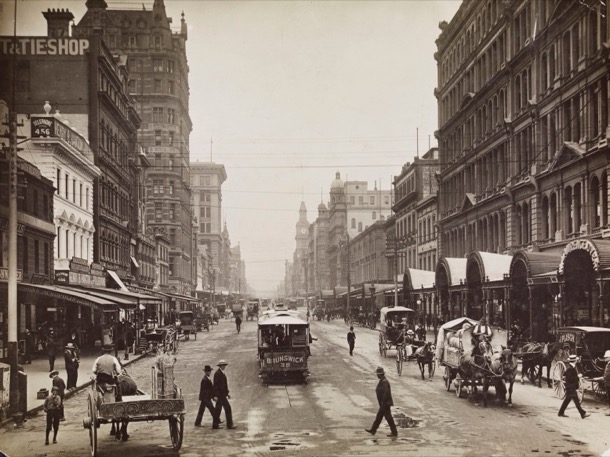
We picture the little farm girls, in their new dresses, in the big noisy city. They would have come on the train, to Flinders Street from Wallan, and walked the three city blocks to the studio.
The city streets would have looked like this:

Their hair would had been in rags overnight. The curls in Sarah, Martha and Emma’s hair have been successful; the others less so. All of them have a ribbon holding their hair back from their face.
The dresses are interesting. The same fabric and pattern seems to have been used for the three eldest girls. Who made them? The next three also have a similar style. All have sturdy boots and frilly pantaloons. These outfits would have been worn to church on Sundays. Did they wear them for the train journey, or change at the studio?
The only other girl, born in 1887, preceded and followed by the seven boys, was Ethel. She wrote diary entries, still held by the Wandong Historical group. Ethel wrote about the boots, which are such a feature of these little girls’ photos. “the rough track across the paddocks and hills, two miles to the little school at Wandong. In wintertime, we had to cross many flooded gullies. We wore strong boots and I was often peeved, as I compared my strong shoes with the dainty ones worn by the other girls at school.”
It was quite an expense to provide boots for so many children.
Our appetite for finding out more about this family is well and truly whetted. We plan further exploration, including an excursion to Wandong.
THREE HOLM SISTERS

These three young women, probably photographed just before the first world war are (left to right) Alfreda, Beatrice and Berta Holm. Alfreda, our maternal grandmother, was the oldest of the three, perhaps just twenty at the time. The three sisters have their long hair swept back in gentle waves, to a loose bun or twist at the back.
We wonder whether they did the white work on their shirts? We know that Beatrice and Berta spent time working in Finders Lane, doing the white embroidery known at the time as “white work”. So much we can only guess at.
They all gaze into the distance: Alfreda with a determined steely gaze, Beat with a quizzical half smile and Bert’s beautiful eyes not quite hiding her vulnerability. We can only guess, as they gaze into a future where world war is imminent.
Alfreda wore her hair long all her life. We can remember her brushing her hair at night and putting it into a long plait.
TWO COATES SISTERS
It’s hard to be a younger sister, but our mother Alice, was the fairly plain younger sister of an extraordinary beauty.
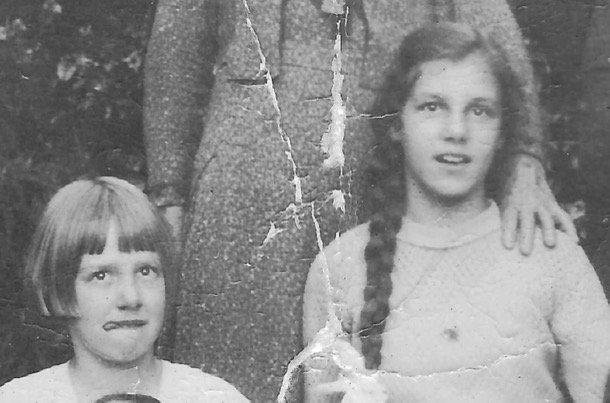
She didn’t have to deal with social media, but, when she was growing up in the 1930s, feminine beauty was important for girls.
Alice was an intelligent and able scholar, and, thank goodness, this was highly valued in her family. Her mother, Alfreda, had made sacrifices and fought for her own education. For their later secondary school, the girls were sent, at huge expense, to a city based secondary school, all the way from Croydon.
Only the wealthiest or most determined families sent their girls to school, after the age of fourteen. At McRobinson Girls’ High School, Marge and Alice were taught by, and shared classes with, the very brightest and best: future women scientists, lawyers and doctors, who would pave the way for our own generation.
But, from her school reports, we see that, while she held her own on the whole, Alice was not exceptional in that auspicious company. And she was crippled, probably her whole life, by a sense of inferiority.
And it is in their respective hair cuts from that time, that we see how the contrast between the two girls was accentuated.
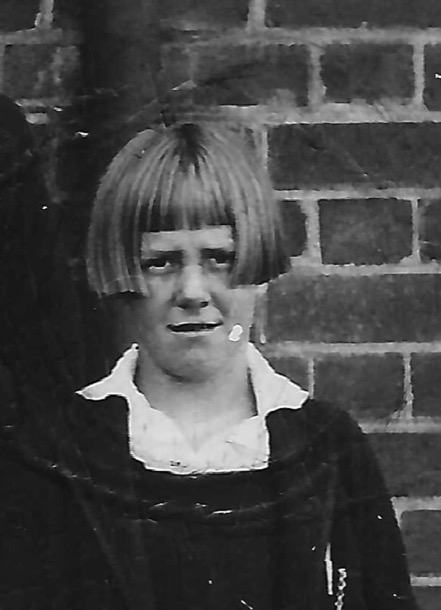
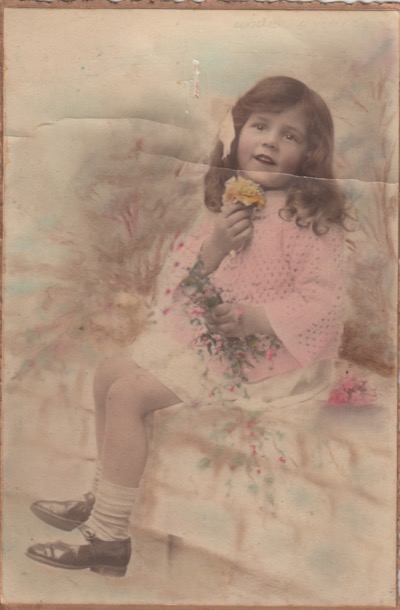

When I stare at those grainy old photos, at Marge’s lush locks, and Alice’s blunt, unfashionable short bob, and straight fringe, I cannot help but ask “Why?”. Why did Alfreda allow her younger daughter to wear such an unflattering style. Why was the difference in feminine beauty accentuated and underlined so prominently by the two hairstyles? How might Alice’s life have been different, had she been encouraged to make the most of her looks, as well as her brains?
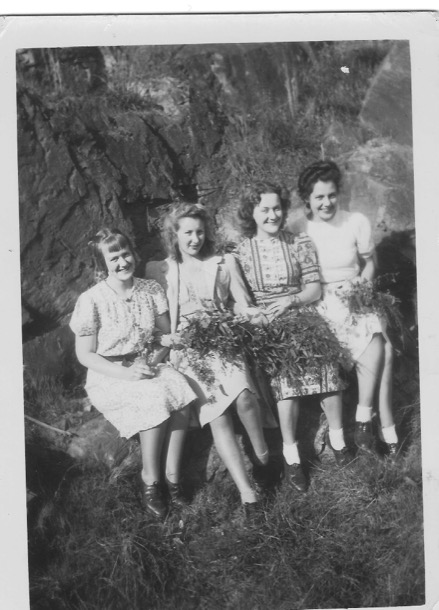
Even as they began working life, both at Maribyrnong Munitions Factory, in 1939, the difference remained. Here Marge is on the far right, and Alice on the far left. Alice is nineteen and Marge twenty-one. But the choice of hairstyle reflects very different attitudes about their appearance:

THE VICTORY ROLL
These two studio photographs of Marge are portraits of a beautiful young woman, but what does the hair tell us?
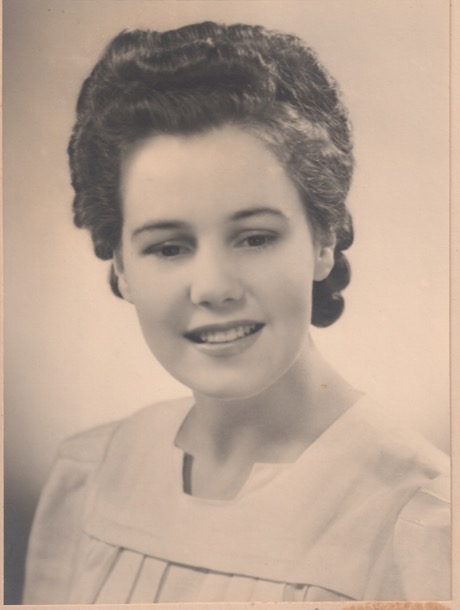

Here, a younger Marge still has very long hair, worn up now, as befitted a young woman who was no longer a child. Pretty curls and barrel curls were the look, and Marge had beautiful, wavy, very cooperative hair and was able to construct ‘the look’ very successfully.
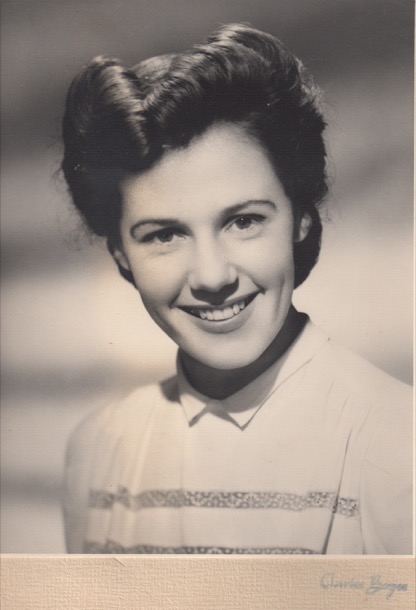

An older Marge, maybe just twenty, posed for this studio photograph as a young woman of the war years, in the “hottest” style of the time. This photograph shows a confident young woman with a job, and presumably many admirers.
During the war, particularly during the Battle of Britain, the ‘Victory Roll’ evolved as a very popular and flattering hairstyle. The style was based on an aerobatic manoeuvre performed by pilots to signify victory. The planes would spin horizontally in celebration. The ‘Victory Roll’ hairstyle would have been difficult to execute, so hours of practice and experimentation was required. The style has stood the test of time, as it is still popular today in ‘retro’ dressing. There are many YouTube videos available with full and detailed instructions.
‘THE SET ‘
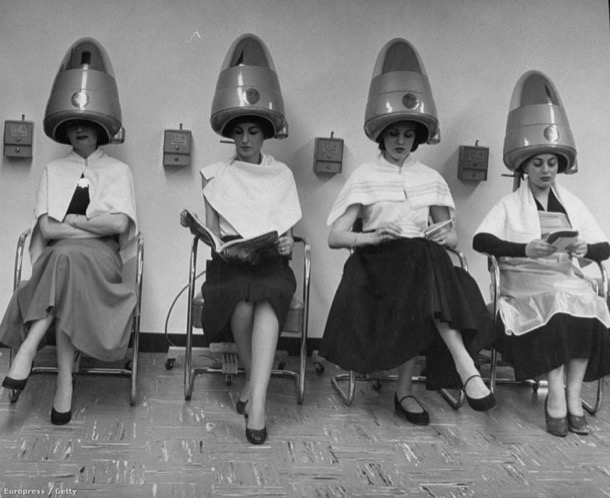
After the second world war, women’s hair fashion was dominated by ‘the set’, often a weekly set. Some women did their own at home, but others, such as our mother Alice, went to their local hairdresser.

The set involved a headful of rollers, tightly wound on wet hair, then dried under a hood dryer. This often took almost an hour, so there was time to read or chat.

Through the ages, and the generations of our family, both sexes’ hair styles have been influenced by the fashion of the day. We have all had cuts, or not. We have curled and permed and coloured and bleached, with varied results.
Today, people are not rigidly restricted to one style, as they were in the past, but have any options.
The lyrics from the musical Hair says it all: .
This post therefore is about hairstyles, but we have allowed ourselves a much broader scope.
ALFRED JOHN COATES

Alfred John Coates, born in 1857, was probably in his late twenties when this photo was taken. He was our maternal great grandfather and was a Methodist Pastor for most of his working life. In this photograph Alfred is a young man in prime of life, dressed in formal dress and sporting the fashion of the day: mutton chop whiskers, carefully manicured to join artfully with the moustache. A man of destiny, the misty ‘bush’ behind him, he stands erect, eyes on the future. At this time Alfred was apparently a boiler maker in Ballarat.
Men’s facial hair trends were changing rapidly in the late 1800s. Long beards were out and clean chins and cheeks and a well-manicured moustache were in. To achieve this look men would need to go to a barber two to three times a week or shave themselves.

Shaving oneself may have been a financial necessity at times but it could also be a dangerous procedure. Shaving was done with a straight steel razor that required care and expertise, not only in the act of shaving the gentleman, but also in the care of the blade. To keep it sharp, the blade was rubbed against a leather or canvas strap before each new shave. As well as the blade, shaving soap, shaving brushes, combs, oils and wax were essential items to achieve the desired effect.
Having a photograph taken in a studio was a special occasion and a relatively expensive exercise. One can imagine that Alfred may have had a trip to the barber to ensure that he looked his best.

Safety steel razor blades that made shaving much easier were not invented until 1895 by an American business man with French heritage.
King C. Gillette invented a low cost blade that was easily replaceable and gave men safety and the freedom to achieve the look desired themselves.
EMMA ELIZABETH DAU
Alfred married Emma Elizabeth Dau in 1888. He was thirty-two and she was twenty Maybe this photo was taken at this time:

Emma is dressed in the style of the day, hourglass figure no doubt with a corseted waist as she gazes into her future with a determined tilt of her chin. Her hair is tightly curled at the front and pulled back into either a bun or pinned up plait.

Unlike the men who had barbers to attend to their needs, there don’t appear to be many ladies' hairdressers. Women had many home implements and potions and maybe sisters and mothers helped each other with their hair.
Young Emma’s tight curls may have been created with curling irons. A curling iron consisted of a metal rod that was held over a flame or burning alcohol to heat it, before wrapping the hair around it. Hey presto, curls!
Later in life, Emma wore her hair in a more relaxed style, loosely pulled back from her face and pinned up into a bun at the back:

When this photo was taken, the height of fashion for women was to wear their hair with more volume at the sides. This was created by using clumps of hair leftover in combs and brushes, to pad out the sides. Emma would not have gone to these lengths in later life, but on her dressing table she would have had a brush, comb, hand mirror and china box, with a lid for the collection of hair caught in brushes or combs. We can remember our grandmother, Alfreda, also having these items on her dressing table. She wore her hair long all her life. During the day it was loosely tied back in a bun, brushed out at night, and the ‘ratts’ collected from the brush and placed in the china box. She then plaited her hair into a loose, single long plait and was ready for bed.
NINE DAU SISTERS
Emma Coates, was born Emma Dau. She was one of seventeen. The first nine of these were girls.
We have three amazing little photos of some of the Dau children. We have spent a long time staring at these images, noticing little details, wondering about the lives of these nine little girls.



The first question we had was, "Were the three photos taken at the same time?". There is such a family resemblance, we weren’t sure at first whether they were different people in the three photos. The carpet gives away that they were taken in the same studio. On the back of one of the playing card sized photos, we see “one shilling per copy”. For context, at that time, a shilling was more than a day’s wage for a working man.
It seems most likely that the three photos were taken on the same day, and they are the nine oldest children, all daughters, of Joachim and Martha Dau, our great, great grandparents.
The photo of the three eldest has writing on the back:

The fact that Martha is misspelt as “marther”, and that no capital letters are used, might be a clue. It was not our mother Alice, nor her parents. None of them would have made such a basic spelling error! The surname is listed as “Dow”.
If those names are correct, then these are the three eldest Dau children. Standing is Sarah, the eldest. the other two are Martha, known as Mishi, and Emma, our great grandmother.
Thanks to the Wandong Historical group, we have the details of nearly all the Dau children.
The next three girls are Bella, Jane and Sophia, followed by Alice, and two others, possibly Annie and Nance, although some sources have Annie and Nance as the same person.
There is no date on these photos, but there are nine girls. The nine first Dau children, all girls were born between 1866 and about 1878. This puts the date of the photos at about 1880, with Sarah, the eldest, aged 14 and the youngest aged 2.
The girls’ father, Joachim, had spelt his surname, Dau. We don’t know the exact date they changed it to Dow, but Frederick enlisted to fight in the Boer War as Dow in 1901, and Arthur, who became a professional soldier, changed his name by deed poll to Dow. The same anti German sentiment that caused the British Royals to change their surname to Windsor from Saax Coburg was no doubt responsible. And yet the Dau spelling persists alongside the Dow spelling, right up until 1929, when Sarah, the eldest wrote about her childhood. Our mother and aunt did not even know about the Dau spelling.
The photographer is listed on the back as Burman, 209 Bourke St Melbourne. The building is still there. This is what it looks like today:

There are a number of old photos by Burman available on line, with that tell-tale carpet visible in some. This one, “Portrait of a Lady”, which uses the same chair as two of our photos, is from C1865.

We picture the little farm girls, in their new dresses, in the big noisy city. They would have come on the train, to Flinders Street from Wallan, and walked the three city blocks to the studio.
The city streets would have looked like this:

Their hair would had been in rags overnight. The curls in Sarah, Martha and Emma’s hair have been successful; the others less so. All of them have a ribbon holding their hair back from their face.
The dresses are interesting. The same fabric and pattern seems to have been used for the three eldest girls. Who made them? The next three also have a similar style. All have sturdy boots and frilly pantaloons. These outfits would have been worn to church on Sundays. Did they wear them for the train journey, or change at the studio?
The only other girl, born in 1887, preceded and followed by the seven boys, was Ethel. She wrote diary entries, still held by the Wandong Historical group. Ethel wrote about the boots, which are such a feature of these little girls’ photos. “the rough track across the paddocks and hills, two miles to the little school at Wandong. In wintertime, we had to cross many flooded gullies. We wore strong boots and I was often peeved, as I compared my strong shoes with the dainty ones worn by the other girls at school.”
It was quite an expense to provide boots for so many children.
Our appetite for finding out more about this family is well and truly whetted. We plan further exploration, including an excursion to Wandong.
THREE HOLM SISTERS

These three young women, probably photographed just before the first world war are (left to right) Alfreda, Beatrice and Berta Holm. Alfreda, our maternal grandmother, was the oldest of the three, perhaps just twenty at the time. The three sisters have their long hair swept back in gentle waves, to a loose bun or twist at the back.
We wonder whether they did the white work on their shirts? We know that Beatrice and Berta spent time working in Finders Lane, doing the white embroidery known at the time as “white work”. So much we can only guess at.
They all gaze into the distance: Alfreda with a determined steely gaze, Beat with a quizzical half smile and Bert’s beautiful eyes not quite hiding her vulnerability. We can only guess, as they gaze into a future where world war is imminent.
Alfreda wore her hair long all her life. We can remember her brushing her hair at night and putting it into a long plait.
TWO COATES SISTERS
It’s hard to be a younger sister, but our mother Alice, was the fairly plain younger sister of an extraordinary beauty.
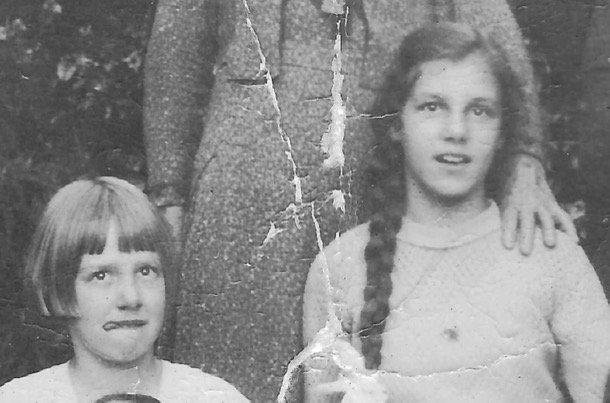
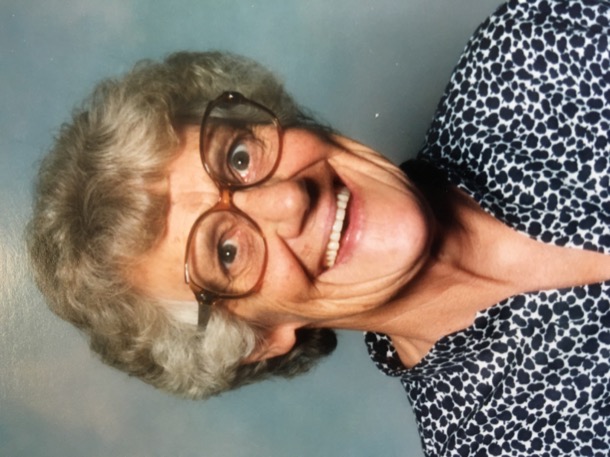
She didn’t have to deal with social media, but, when she was growing up in the 1930s, feminine beauty was important for girls.
Alice was an intelligent and able scholar, and, thank goodness, this was highly valued in her family. Her mother, Alfreda, had made sacrifices and fought for her own education. For their later secondary school, the girls were sent, at huge expense, to a city based secondary school, all the way from Croydon.
Only the wealthiest or most determined families sent their girls to school, after the age of fourteen. At McRobinson Girls’ High School, Marge and Alice were taught by, and shared classes with, the very brightest and best: future women scientists, lawyers and doctors, who would pave the way for our own generation.
But, from her school reports, we see that, while she held her own on the whole, Alice was not exceptional in that auspicious company. And she was crippled, probably her whole life, by a sense of inferiority.
And it is in their respective hair cuts from that time, that we see how the contrast between the two girls was accentuated.
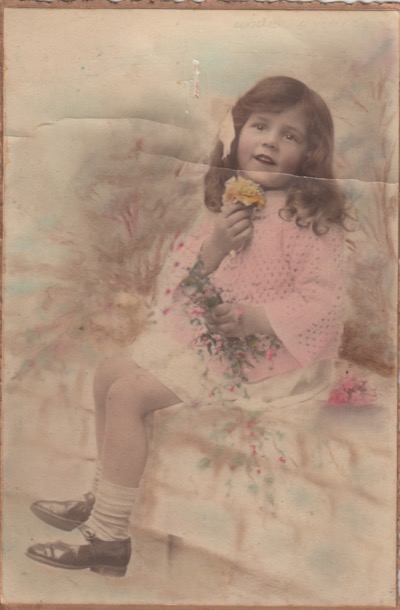

When I stare at those grainy old photos, at Marge’s lush locks, and Alice’s blunt, unfashionable short bob, and straight fringe, I cannot help but ask “Why?”. Why did Alfreda allow her younger daughter to wear such an unflattering style. Why was the difference in feminine beauty accentuated and underlined so prominently by the two hairstyles? How might Alice’s life have been different, had she been encouraged to make the most of her looks, as well as her brains?
Even as they began working life, both at Maribyrnong Munitions Factory, in 1939, the difference remained. Here Marge is on the far right, and Alice on the far left. Alice is nineteen and Marge twenty-one. But the choice of hairstyle reflects very different attitudes about their appearance:

THE VICTORY ROLL
These two studio photographs of Marge are portraits of a beautiful young woman, but what does the hair tell us?

Here, a younger Marge still has very long hair, worn up now, as befitted a young woman who was no longer a child. Pretty curls and barrel curls were the look, and Marge had beautiful, wavy, very cooperative hair and was able to construct ‘the look’ very successfully.

An older Marge, maybe just twenty, posed for this studio photograph as a young woman of the war years, in the “hottest” style of the time. This photograph shows a confident young woman with a job, and presumably many admirers.
During the war, particularly during the Battle of Britain, the ‘Victory Roll’ evolved as a very popular and flattering hairstyle. The style was based on an aerobatic manoeuvre performed by pilots to signify victory. The planes would spin horizontally in celebration. The ‘Victory Roll’ hairstyle would have been difficult to execute, so hours of practice and experimentation was required. The style has stood the test of time, as it is still popular today in ‘retro’ dressing. There are many YouTube videos available with full and detailed instructions.
‘THE SET ‘
After the second world war, women’s hair fashion was dominated by ‘the set’, often a weekly set. Some women did their own at home, but others, such as our mother Alice, went to their local hairdresser.

The set involved a headful of rollers, tightly wound on wet hair, then dried under a hood dryer. This often took almost an hour, so there was time to read or chat.

Through the ages, and the generations of our family, both sexes’ hair styles have been influenced by the fashion of the day. We have all had cuts, or not. We have curled and permed and coloured and bleached, with varied results.
Today, people are not rigidly restricted to one style, as they were in the past, but have any options.
The lyrics from the musical Hair says it all: .
‘Gimme a head with hair
Long beautiful hair
Shining, gleaming,
Streaming, flaxen, waxen’
blog comments powered by Disqus

